The FILE adapter in BizTalk is used for sending and receiving messages by reading from or writing to files in a specified directory. It is a commonly used adapter for integrating file-based systems with BizTalk Server. This section explains how to monitor file locations associated with the ports utilizing the "FILE" adapter transport type.
Setting up File Monitoring
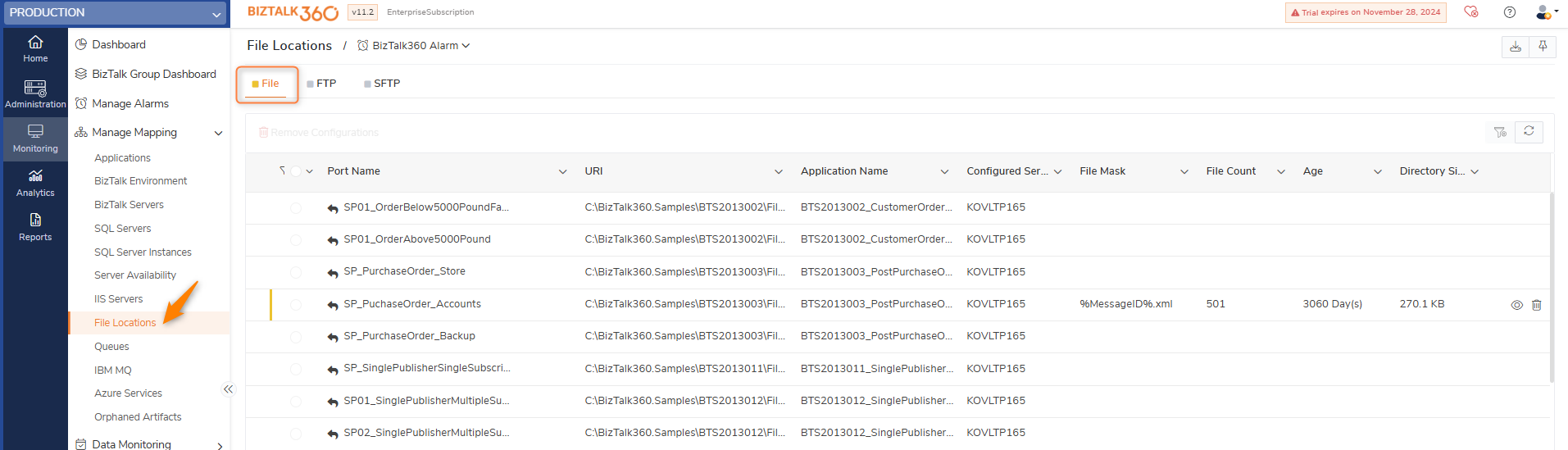
You can follow the below steps to configure File monitoring:
- Log in to the BizTalk360 application.
- Select the environment and navigate to Monitoring->Manage Mapping->File Locations.
- In file location section ,you can see three tabs each containing port details of their respective adapters, which are File, FTP, and SFTP.
- Click the 'File' tab to monitor File locations.
- Select the Alarm name (Manage Alarms) from the drop-down, which you would like to associate the file location for monitoring.
- The ports (receive locations and send ports) that use the "FILE" adapter are displayed in a grid.
Click on any port to configure the file for monitoring. The configuration includes the following:
- Basic File configurations
- Monitoring Rules
- Restart Host Instance (Only applicable for Receive Locations ).
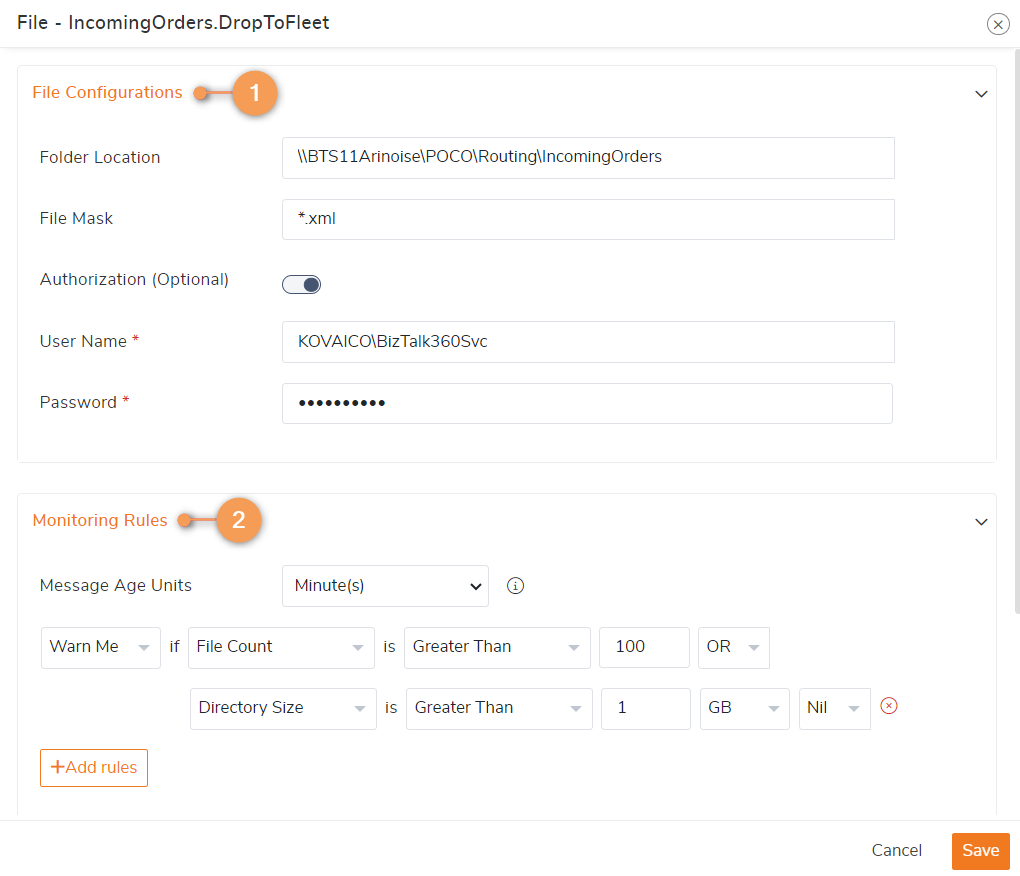
1. Basic File Configurations
- Respective Folder Location and the File Mask will be listed.
- File Mask : If the folder might receive multiple types of files, but you wants to monitor only a particular type of files, then you can overwrite the File Mask. All file extensions (e.g., CHPAPO*.txt, *.txt, * . *, *outbound322*, PPI*, Test*. *) and macros patterns are supported in File monitoring by making the file mask field editable.
- Authorization : By default, the Monitoring service account is used for authorizing and accessing the file. However, if you are monitoring sensitive files and folders that require separate authorization, you can enable the Authorization option and provide a Username and Password for authentication.
2. Monitoring Rules
- You can configure the Warning and Error threshold rules for different metrics (File Count, Directory Size and Age) to monitor.
For example, let's consider a BizTalk application called "Order Processing" that receives XML orders from suppliers. These orders are dropped into a folder named "IncomingOrders" on the BizTalk server. To ensure smooth order processing and prevent disruptions due to file overload or insufficient disk space, you can create threshold rules for monitoring the File count and Directory Size as mentioned in the below image.
The Count, Age, and Directory Size fields appear in the File Location grid only after the file location has been successfully configured.
If the specified location is not reachable then, system could not continue to monitor the metrics (File count , Directory Size ) . In this case the monitoring status will be set to Critical .
Monitoring Absolute Path vs Network Shared Path
File configurations can have either Absolute path or Network shared path . Let's explore how each option works in BizTalk360.
Absolute Path:
An absolute path refers to the precise location of a file or directory starting from the root directory. In simpler terms, it represents the complete path starting from the root directory (E.g. "C:") of the file-system. Since an absolute path points to a specific file location, in BizTalk, the server where files are processed is determined by the host instance. The host instance is selected based on the specified handler, which is either the send handler for a send port or the receive handler for a receive location associated with the artifact.
BizTalk360 monitors file locations in a similar way. It identifies the host instances associated with the artifact and monitors the file locations on the servers where the host instances are configured. Let’s explore how BizTalk360 monitors file locations across different setups.
High-Availability (HA) Host Instances Set-up:
In a High-Availability (HA) setup with host instances configured on multiple servers, BizTalk360 monitors the file location on all servers where the host instances are set up. This ensures continuous monitoring even if one of the servers encounters an issue.
For example, let's say the file location is specified as "C:\Kovai\Purchase_Orders\Inbound" and the host instances are configured on "Server_A" and "Server_B".
BizTalk360 monitors the file location on both "Server_A" and "Server_B" simultaneously. If the files are processed without any issues on "Server_A" but are stuck in "Server_B" then BizTalk360 will trigger the alert for "Server_B" and vice-versa. The monitoring results for each server can be viewed in detail on the threshold summary page. 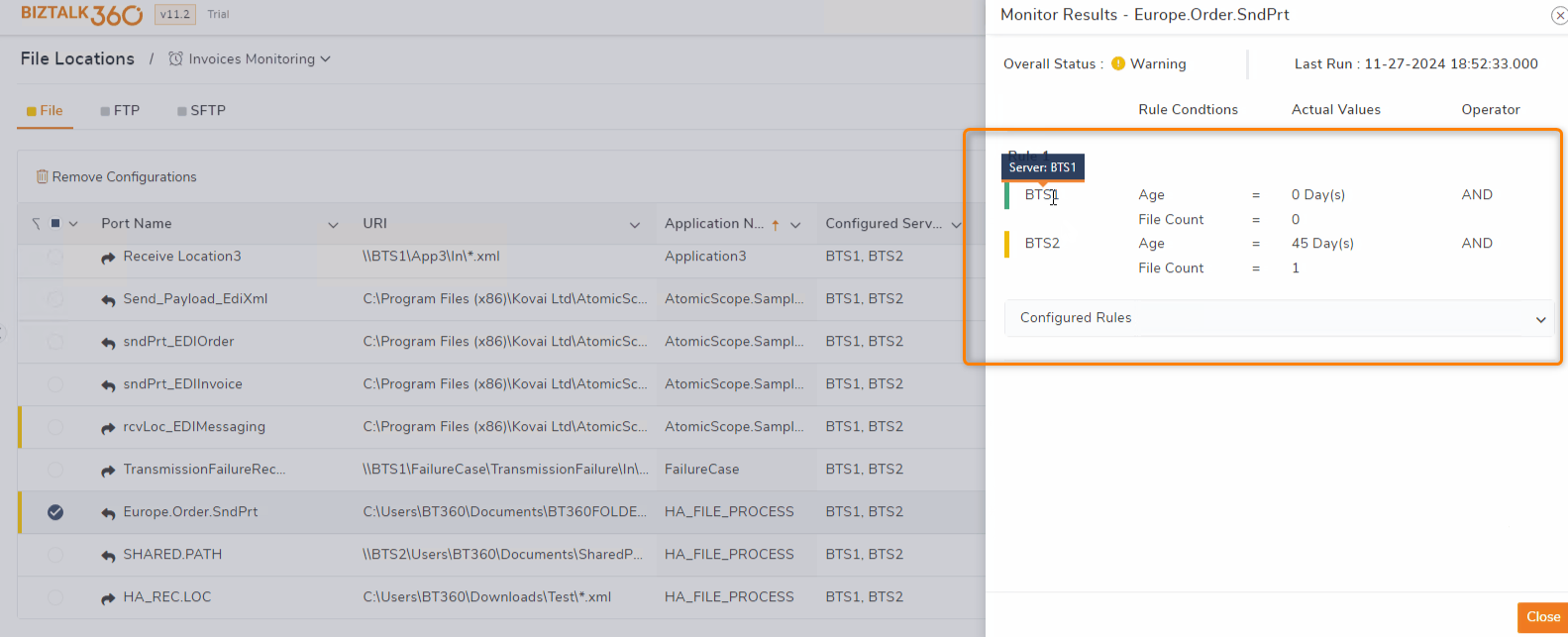
Cluster Host Instances Set-up:
If the associated host instances are clustered, BizTalk360 monitors the file location on the server where the host instance is currently running. If no host instance is running at that moment, BizTalk360 will check the file location on all servers where the host instances are configured.
For example, Let's say the file location is specified as "C:\Kovai\Purchase_Orders\Inbound\" and the host instances are configured on "Server_A" and "Server_B".
- If the host instance is running on "Server_A", BizTalk360 monitors the file location only on "Server_A".
- If no host instance is running, BizTalk360 monitors the file location on both "Server_A" and "Server_B".
Network Shared Path:
A network shared path is a folder location that can be accessed by multiple users or computers over a network. It allows files to be shared and accessed by different servers. In a network shared path setup, the folder location must be accessible by the BizTalk360 Monitoring Service to ensure proper monitoring.
For example, let's say the folder location is specified as "\\Server_B\SharedFolder\Kovai\Purchase_Orders\Inbound". In this scenario, BizTalk360 will directly monitor the shared folder located on the specified server "Server_B".
Here is a GIF demonstrating how file monitoring works based on the setup:
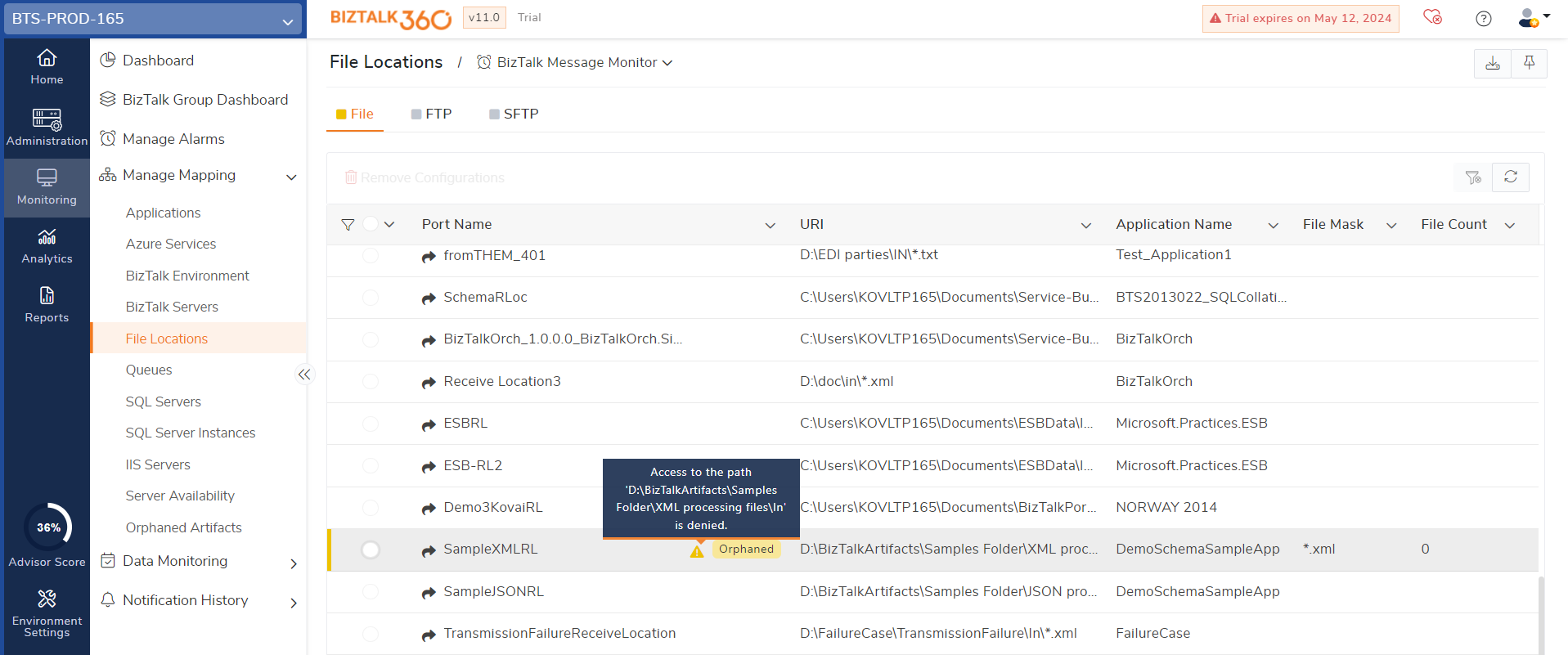
Orphaned File Locations
If BizTalk360 cannot connect to the File location, the configuration will be considered Orphaned and monitoring the metrics will not be carried out. File locations may become orphaned under the following circumstances:
- When the monitoring service account or the configured user account doesn't have permission to access the file.
- When the configured file location is removed or renamed on the machine but not updated in BizTalk360 configuration.
- When the respective URI is modified in the BizTalk Admin Console but not updated in BizTalk360 configuration.
- When the server hosting the shared path goes down, the path will become orphaned.