BizTalk360 has a powerful operational governance and auditing capability to maintain the logs of the user activities in the system. This feature helps the BizTalk administrators to find out "Who did what" in the environment over a period of time. Consider a few example scenarios when a support user:
- Accidentally stops a host instance
- Terminated a suspended service instance
- Accidentally unenlisted an orchestration in the application
In these situations, if the user action is recorded and logged as an event, it will help the administrator to identify the root cause of the issue. Only from BizTalk Server 2020, the activities are audited in the BizTalk Administration console. Other lower versions of the BizTalk server do not audit any activities. This leaves organizations to run their support purely based on trust, which may not be ideal in some mission-critical situations like Healthcare, Financial services, etc.
What artifacts can be audited in BizTalk360
BizTalk360's has the capability to audit the following areas:
- Application operations
- Application Artifacts operations
- Service instance operations
- Host instance operations
- BizTalk/SQL Server operations
- ESB Message Activities
- Business Rules Activities
- Tracking Activities
- Message Content Views
BizTalk Application Artifacts Administration audit
BizTalk Server uses a publish/subscribe messaging engine architecture where all incoming messages are published to the MessageBox database and picked up by the send ports (groups) and/or orchestrations. The three main components of this architecture are:
- Receive locations/Receive Ports
- Orchestrations
- Send Ports (Groups)
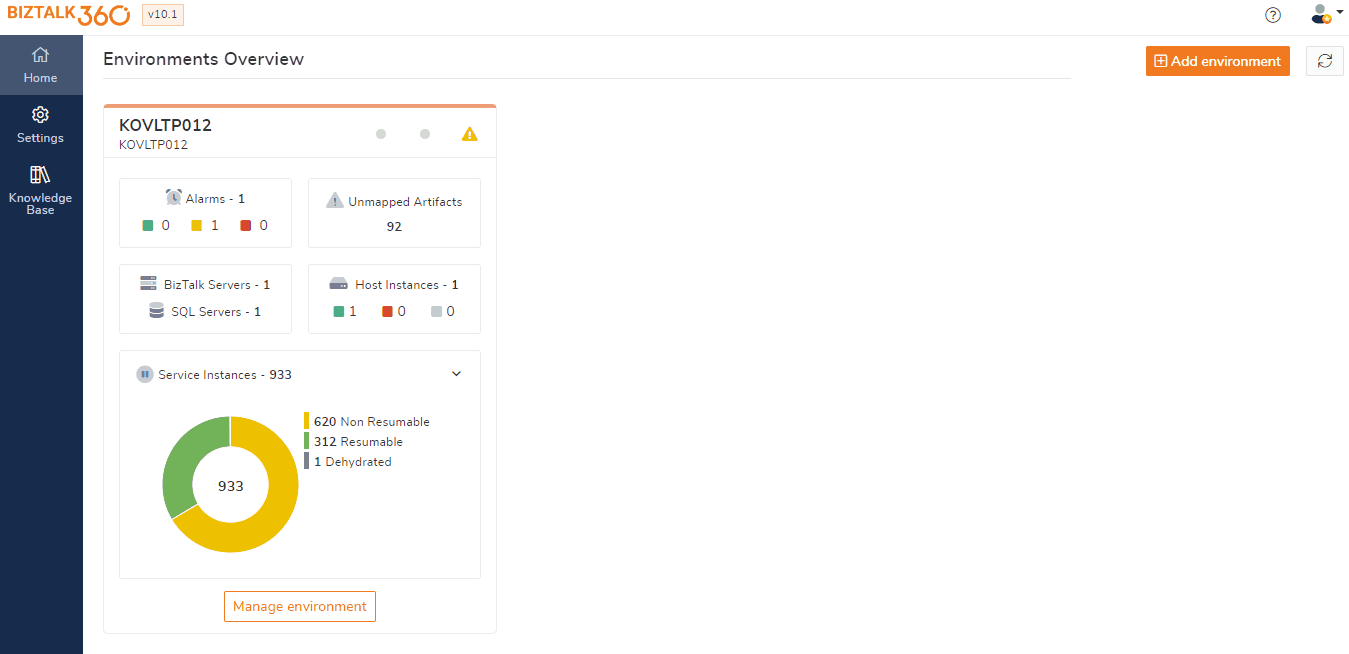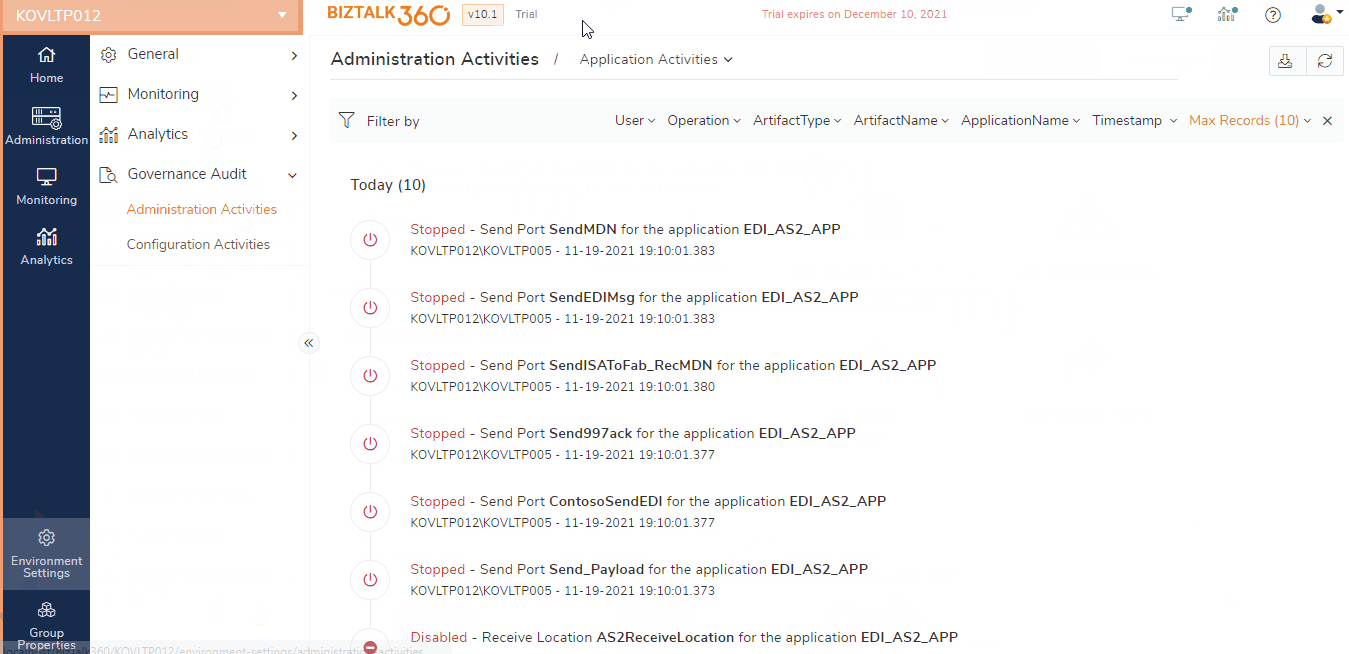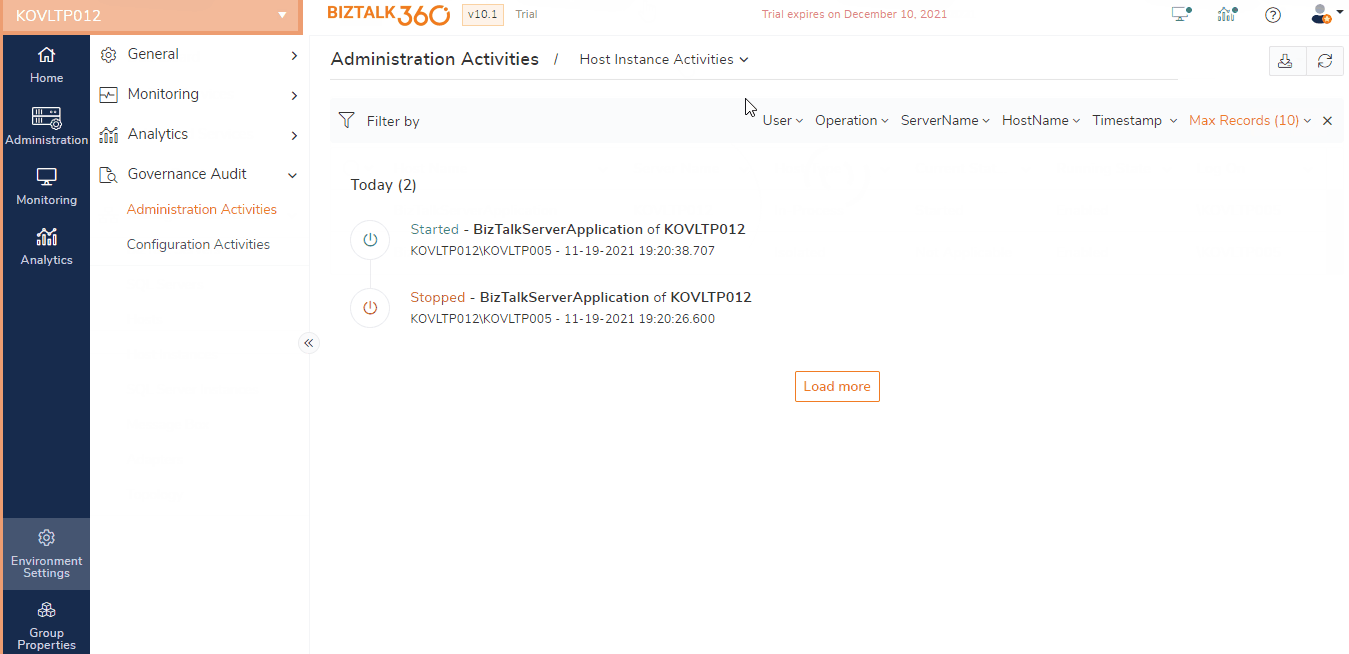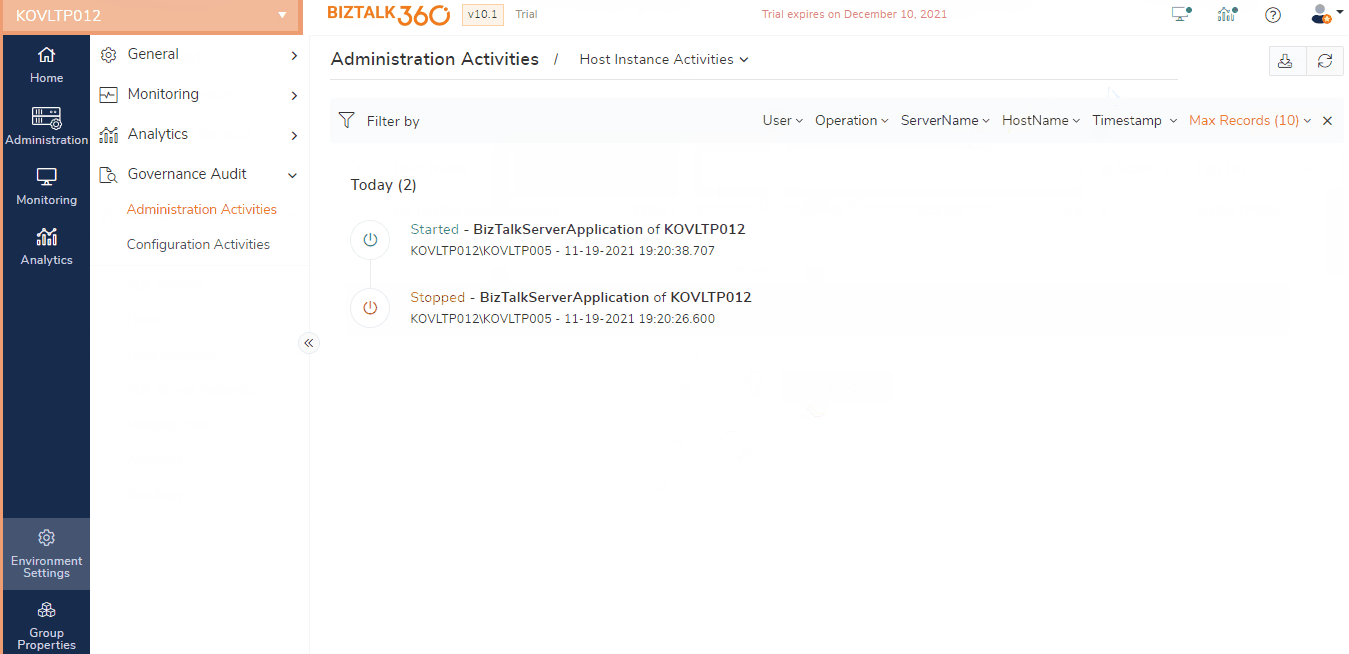
These components are isolated from one another and BizTalk Server offers the flexibility to control (start, stop, enable, disable, etc.) each one of them individually. Let's assume we have an application PurchaseOrderProj that uses, say, an MSMQ adapter configured on the receive port (ReceivePort) to receive the messages in BizTalk Server. Accidentally (or intentionally) if the support user disables the receive location, it will stop BizTalk Server from polling messages from MSMQ. This will result in serious consequences for the business. Therefore, it is critical for the organizations to collect the audit log of the activities that are done on application artifacts like send ports, receive locations, and orchestrations.
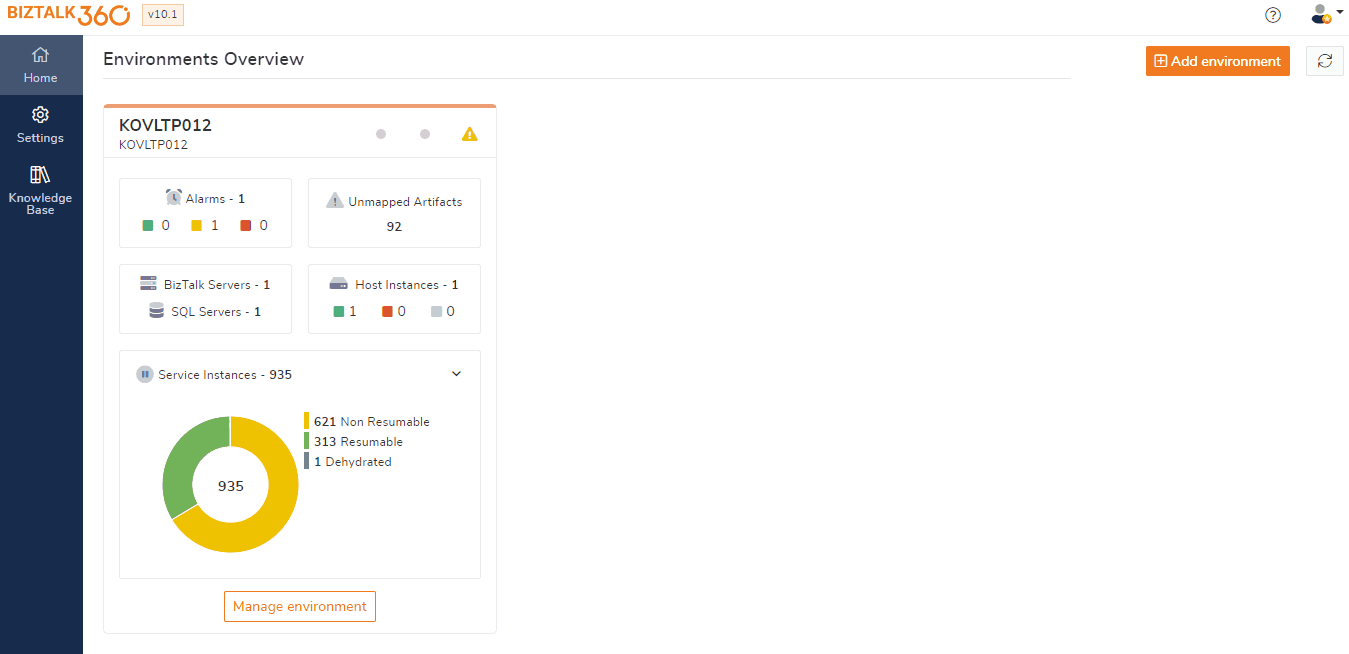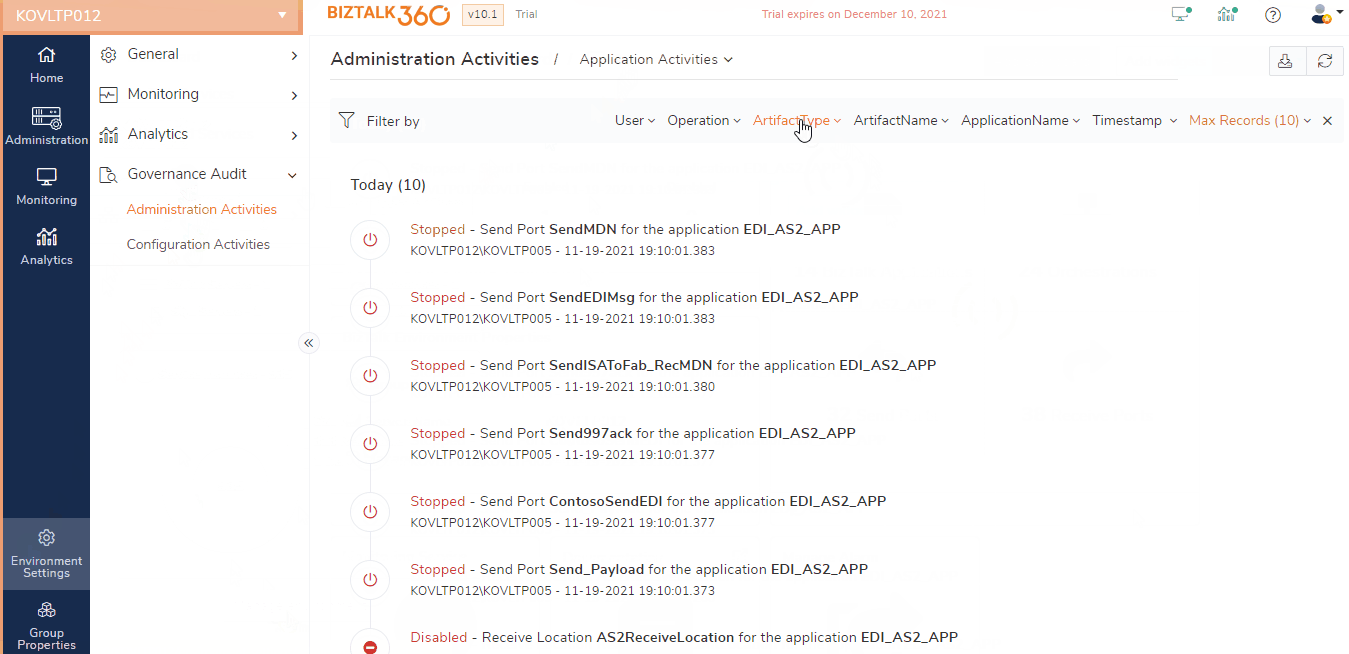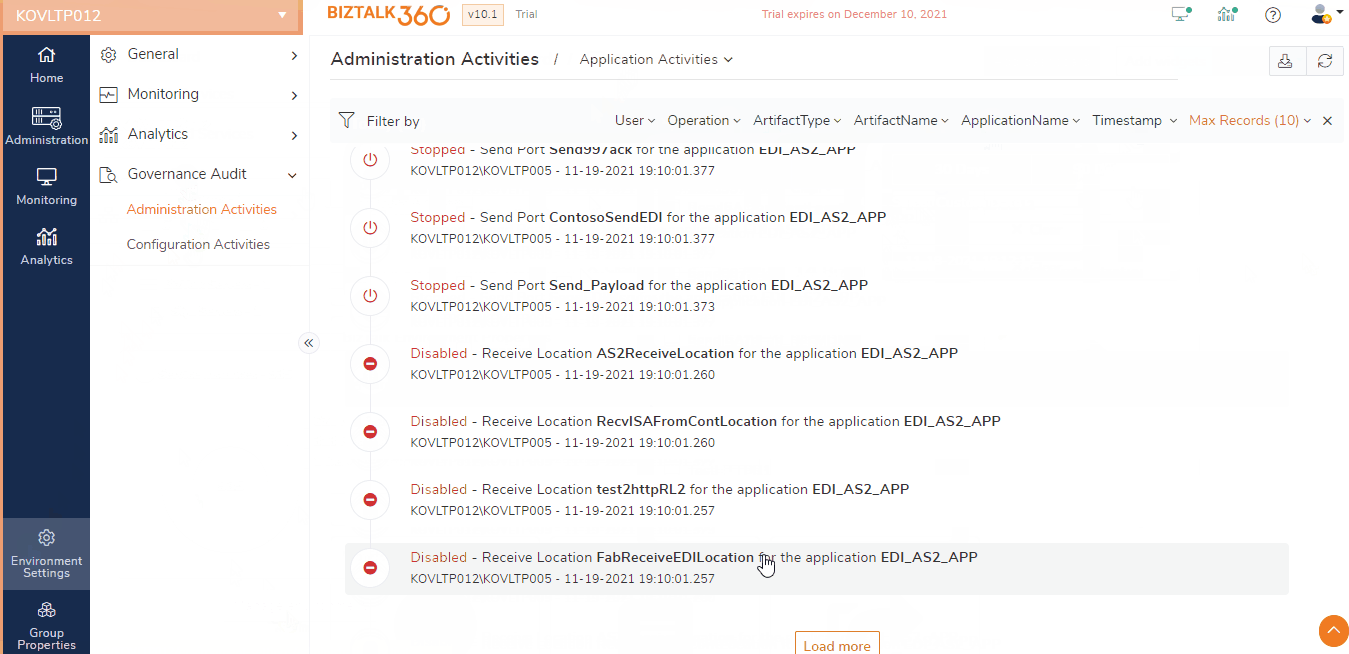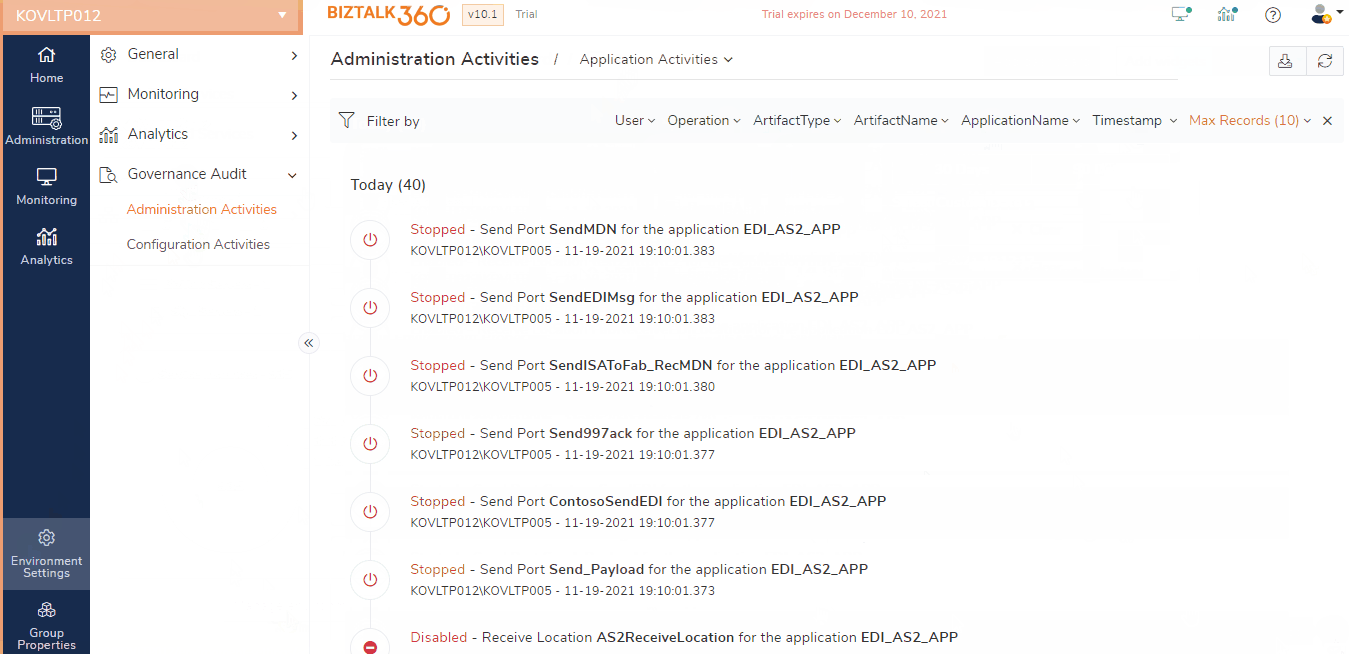
BizTalk360 by default audits all the activities performed by the support person on the application receive location, orchestration, and send ports. Following are the list of events captured by BizTalk360 for auditing:
- Enable/disable of receive locations
- Start/Stop/Enlist/Unenlist of orchestrations
- Start/Stop/Enlist/Unenlist of send ports
Service Instance Administration audit
It is a best practice to keep an eye on the status of the service instances in the BizTalk environment. Too many service instances (in any state like suspended, ready to run, etc.) and not clearing up periodically in the environment might highlight some potential problems. Example: Too many suspended service instances will bloat the MessageBox database and affect the overall performance of the system over a duration of time.
Therefore, it is the responsibility of the support person to make a decision whether to resume the suspended service instances or to terminate them. But there may be chances when the support person may accidentally terminate a service instance that must be resumed. This could cost the business a potential transaction. Therefore, it is important for the organization to set up auditing mechanisms to record the user actions to understand "Who did what" in the environment. By clicking on the eye icon user can able to view the service instance audit details.
Host Instance Administration audit
A BizTalk Host is a logical set of zero or more BizTalk runtime processes, which you can configure to run items such as adapter handlers, receive locations (including pipelines), and orchestrations. A host instance is a physical process (NT Service) that is created in BizTalk Servers where the message processing, receiving and transmitting occurs.
BizTalk Server provides the capability for the users to control the state of the host instances (start, stop, enable, disable) through the BizTalk Server Administration Console. Any of these operations can have consequences on the business operations. For instance, if a tracking host instance (which is responsible for moving DTA and BAM tracking data from the MessageBox database to DTA and BAMPrimaryImport databases) is accidentally stopped, the data transfer will not happen as expected. This will bloat up the MessageBox database size and result in performance issues.
On a different example, if a host instance responsible for receive or transmitting messages is kept in a disabled or stopped state, then BizTalk Server will not receive or transmit messages, which could be serious. So, it becomes more important to keep track of the health of the BizTalk host instance by monitoring as well as keep an eye on who is performing any activities on the host instance.
BizTalk/SQL Server Administration audit
In each BizTalk and SQL server that exists in a BizTalk Server environment, many Windows NT services exist. These services can be of critical importance for the well-being and properly working of the BizTalk Server environment. Think of, for example, the following services that must be running:
- Enterprise Single Sign-On service
- BizTalk Host instances (BTSSVC* services)
- SQL Server
- SQL Server Agent
- Internet Information Services
BizTalk360 enables you to access and manage the Windows NT Services for the BizTalk and SQL servers that are part of the BizTalk Server environment. You can find these capabilities in the Operations section, under Manage Infrastructure, and then:
- BizTalk Servers
- SQL Servers
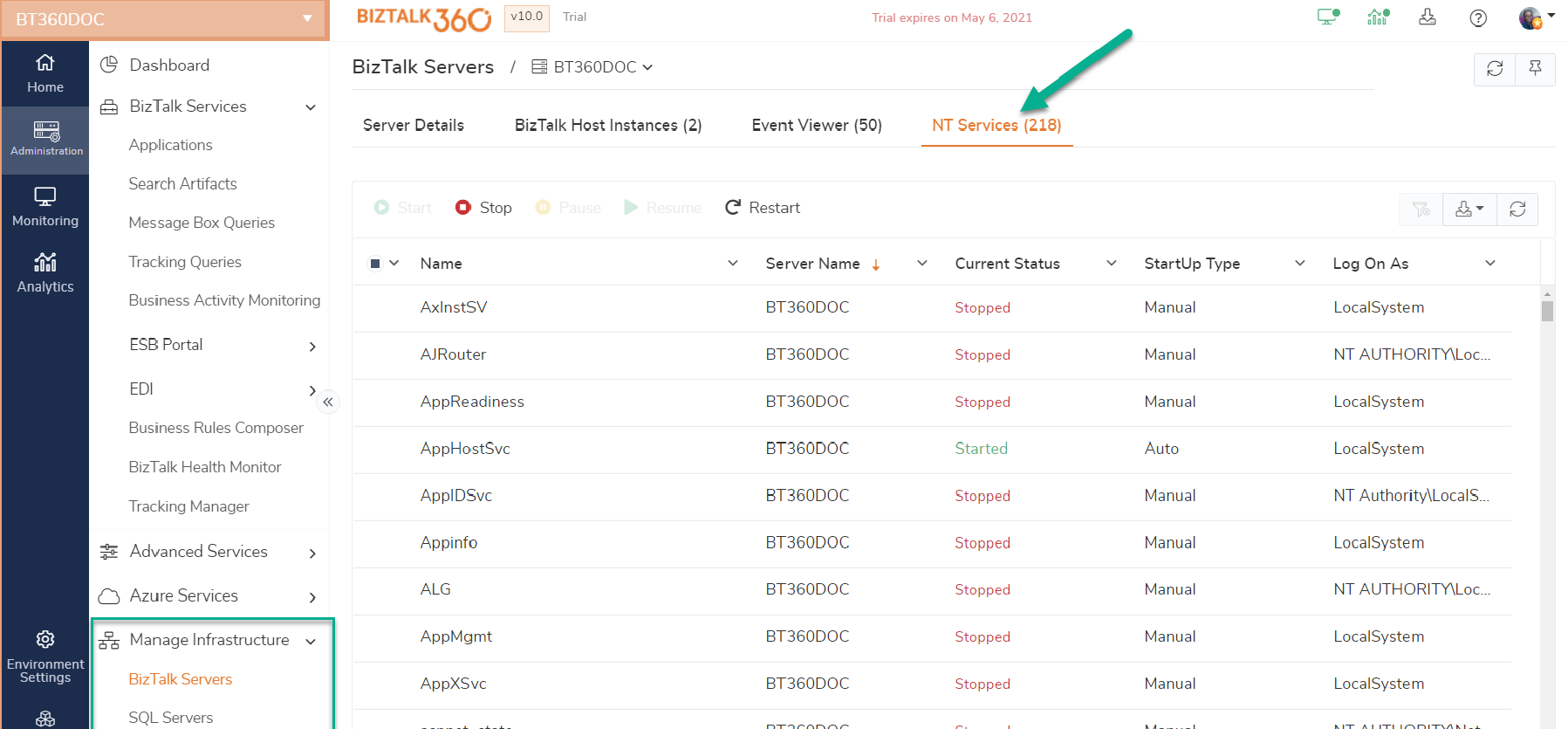
The following operations are audited by BizTalk360:
- Start - Starting a Windows NT Service
- Stop - Stopping a Windows NT Service
- Restart - Restarting a Windows NT Service
ESB Message activity audit
BizTalk360 has the capability to audit message edit/resubmit activities in the in-built ESB Portal. Whenever the logged-in user tries to resubmit a message to a particular receive location and if the resubmit activity happens successfully, an audit record will be created under the "ESB Message Activities" section BizTalk Activities in Governance Audit module of BizTalk360 with the result as "202-Successfully submitted to ". Even if they submit operation does not happen as expected, an audit log would be created under ESB message activities with the result as "500-Failure submitting to ". The audit information gets logged with the action that was performed on the message, the message id, the result of the activity, date time stamp when the operation was performed, and details of the user who performed the action.
In addition to auditing the ESB message activities, BizTalk360 offers added functionality to users to be able to view the details of the message that was submitted. The user with access to the Governance Auditing module in BizTalk360 can simply click the value under the 'Message ID' column to view the message details such as general message information, content properties, and context properties.
Business Rules activity audit
With the traditional BizTalk Rules Composer feature, the process is long and tedious when it comes to saving/publishing, and deploying the business rules. The "Business Rules Composer" feature comes out of the box with the product. With this feature, the business user no longer needs to contact IT to add/modify a rule and publish/deploy them. Any user who has access to Business Rules Composer can create new rules, save, publish and deploy policy directly to the production environment. So, it becomes important to track the changes made in the business rules and as well as keep an eye on who is performing any activities in the business rules composer.
Audit Tracking activities
BizTalk360 provides the consolidated Tracking Manager screen which lists the tracking details for the artifacts of the applications, which also allows users to enable/disable the tracking on the artifacts like Receive Ports, Send Ports, Orchestrations, Schemas, Pipelines, and Policies of the BizTalk Application. Users can also manage the Global tracking from BizTalk360 UI . Tracking is a key feature in BizTalk Server, both the global and application level tracking activities done from BizTalk360 are audited.
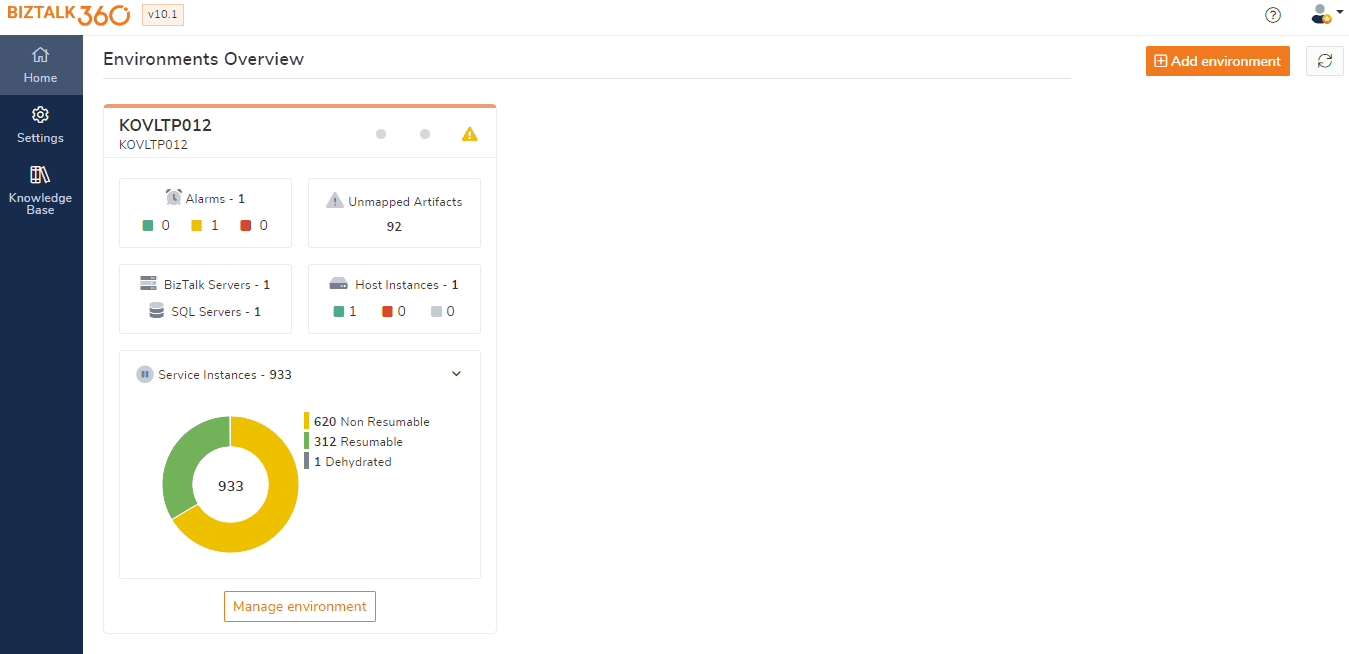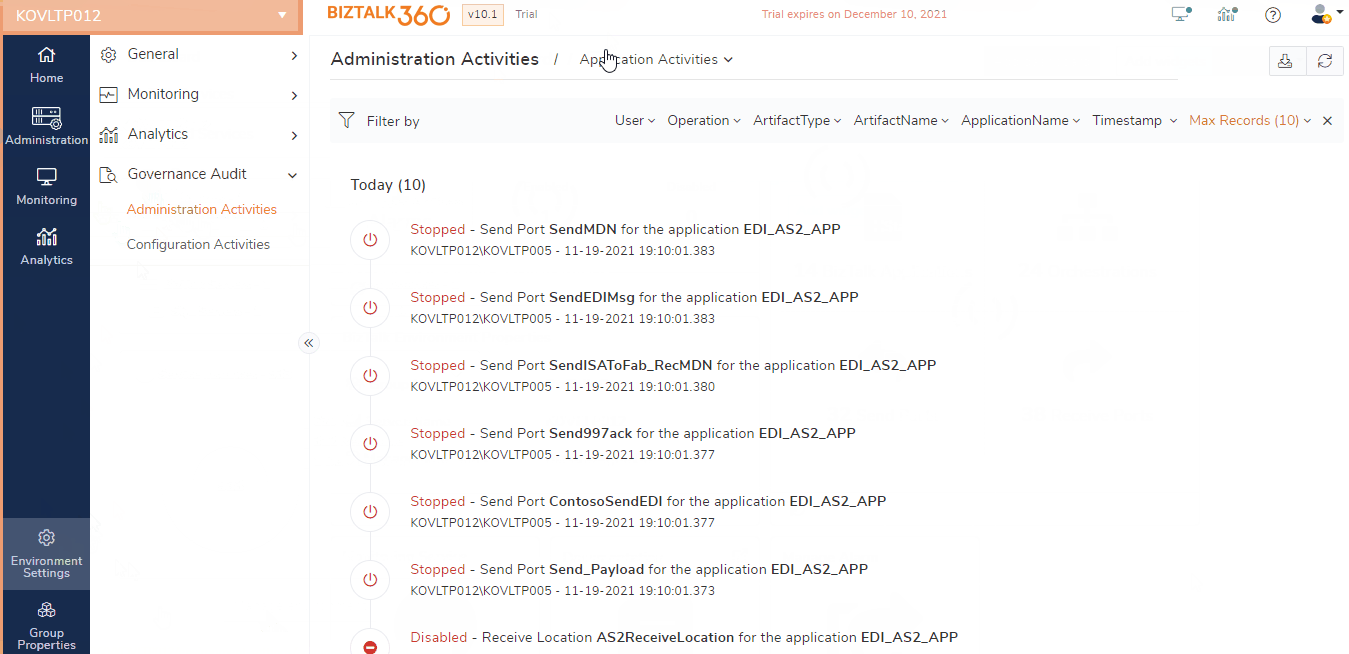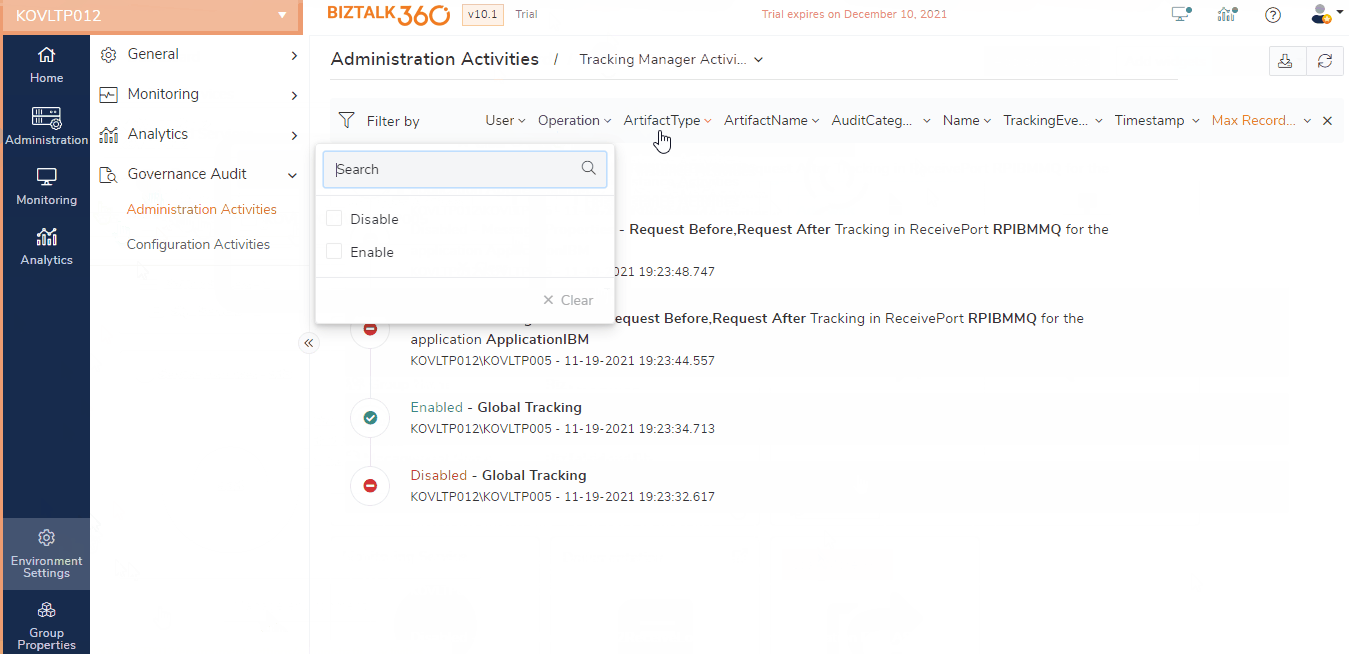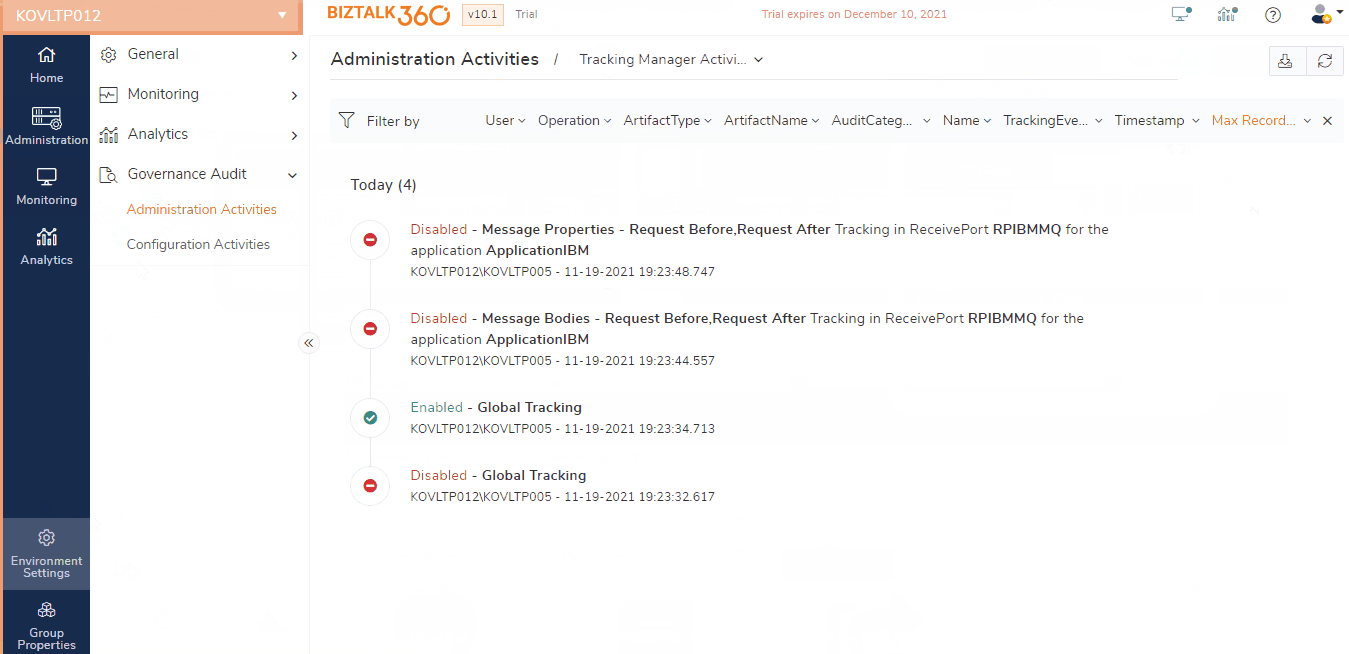
Audit Message Content View
Users can view the message content of the particular instance in multiple sections in BizTalk360 such as Message Box Queries, Graphical Message Flow, ESB. The messages certainly hold the sensitive data so to tighten the security, if any message contents are viewed by the user the same will be audited under the auditing section of the respective module.
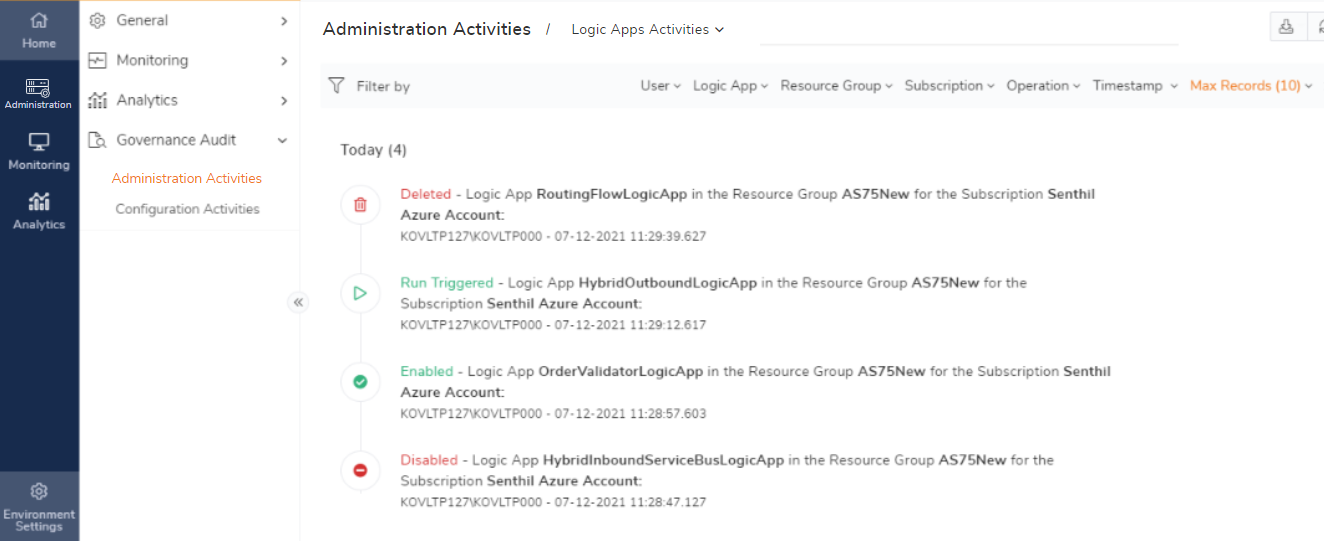
Audit Logic Apps
The Logic Apps can be easily managed and monitored from BizTalk360 by configuring the Azure subscription. BizTalk360 users who have permission to access Logic Apps can only view the details of available Logic Apps under the configured subscriptions, Users who have permission to manage Logic Apps can perform below Logic Apps operations through BizTalk360, all these actions are audited under Logic Apps activities.
- Enable /Disable
- Trigger Runs
- Resubmit
- Delete
BizTalk audit integration with BizTalk360
From BizTalk360 v10.2 you can view the BizTalk audit data in the BizTalk360 governance and audit section. This is only supported from BizTalk Server version 2020. To use this feature you need to enable auditing in the BizTalk admin console. The audited data are stored in the BizTalk table , there is no specific UI to view the data. With this integration in BizTalk360 auditing section, you can visualize the activities that are performed in the BizTalk admin console.
Steps to be followed
- Enable Auditing in Admin console. you can find this under BizTalk group settings
- You need to configure what audit activities you want to view in the BizTalk360 auditing section. Navigate to Environment settings-> Governance Audit->Click Audit Configuration, where you can specify what administration activity needs to be audited
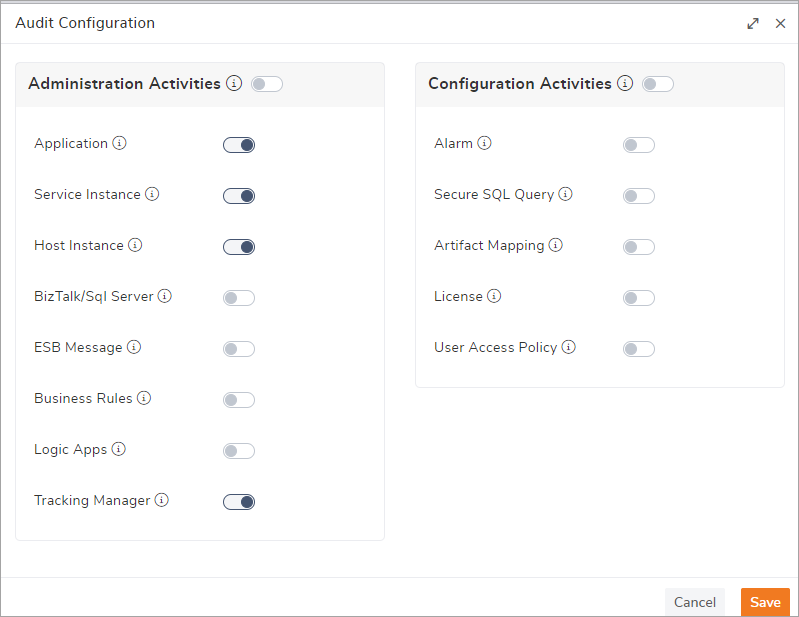
- Ensure the Subservice BizTalkAudit is running. you can find this subservice under Settings->Manage Services->Monitoring Services->Advanced services. This subservice will pull the data from the BizTalk audit table on every 5 minutes.
Below operations are audited in BizTalk, which will get listed in the BizTalk360 audit section
- Application - Create, Delete, Import, Start and Stop
- Send Port - Create, Start, Stop, Enlist, UnEnlist, Delete, Move to application, Tracking
- Receive Port – Create, Delete, Move to application, Tracking
- Receive Location - Create, Enable, Disable, Delete, Move to application
- Orchestration – Start, Stop, Enlist, Unenlist, Remove, Move to application, Tracking
- Resources – Remove, Move to Application
- Service Instance- Suspend, Terminate, Resume
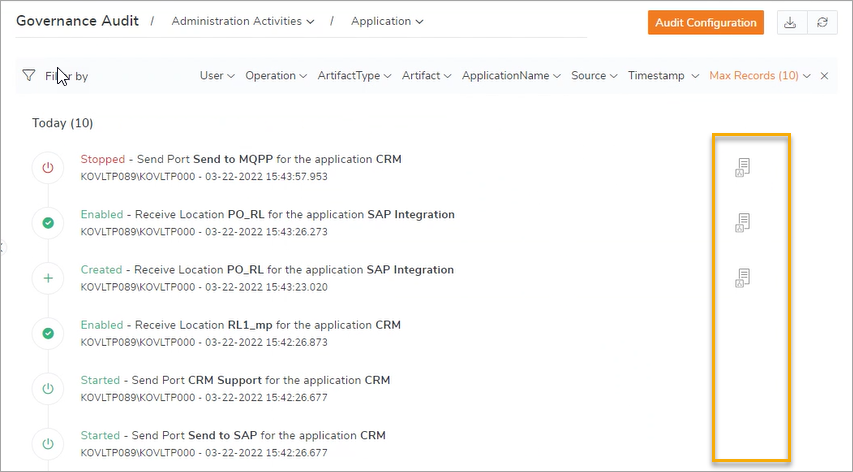
In the above image, you can easily see which user has done the operation along with the time period. The auditing source whether the operation is performed in BizTalk360 or BizTalk is indicated through the BizTalk icon.
Use the filter option to drill down the auditing data. The auditing data can be exported for further actions using the Export to Excel or Export to PDF option on top of the grid.