Auditing BizTalk360 Activities
BizTalk360 Auditing is implemented to audit the activities done by users of BizTalk360. Through this feature, users can have a clear view about, which user has made which changes in BizTalk360.
Activities performed in the following sections are audited:
Manage Alarm
Manage Mapping
Secure SQL Queries
BizTalk360 Licenses
User Access Policies
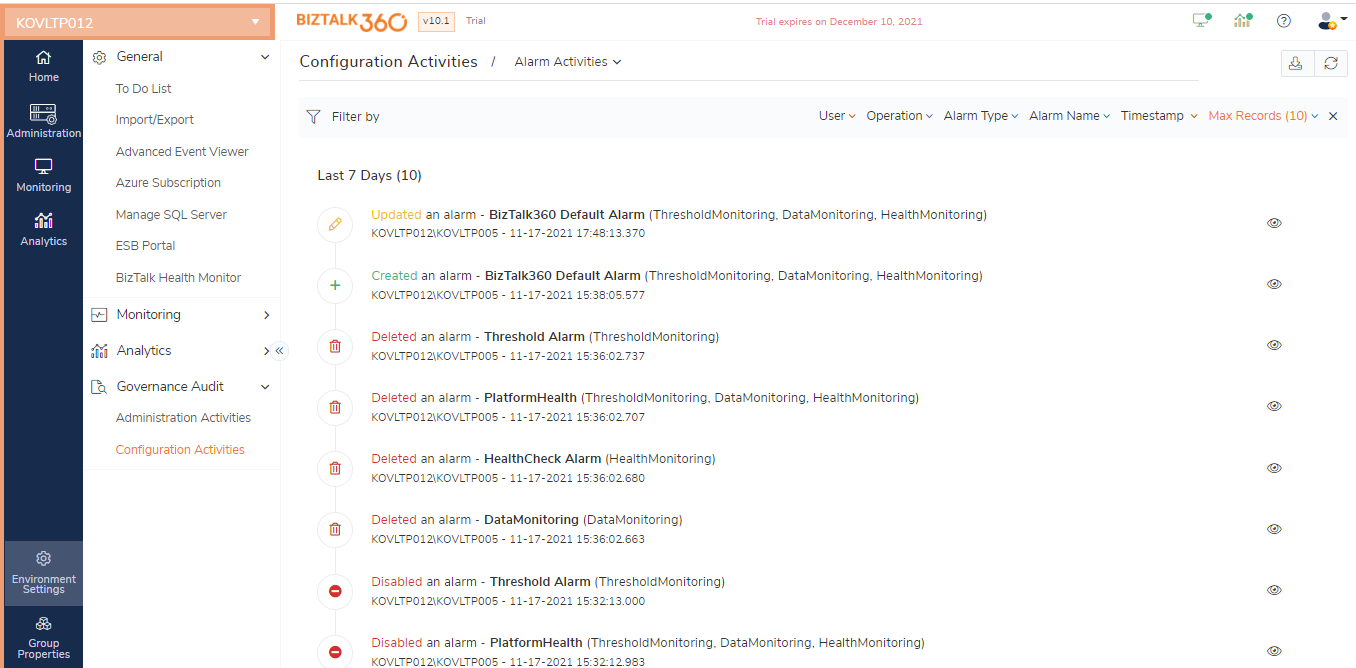
Manage Alarm audit
Being able to manage alarms in BizTalk360, is an important feature in the monitoring section, in which users need to create an alarm as a first step to monitor the BizTalk server’s Application Artifacts, BizTalk /SQL Environments, Folder locations, Queues, Azure Services, etc.
The following operation activities done at the Manage Alarm section will be audited:
Create - Alarm creation includes creating a new alarm, copying an existing alarm, and creating a Quick Alarm
Update - Update operations include changing the alarm configuration details, changing the status (Enable/Disable) of an alarm
Delete - Delete operations include deleting a single or multiple alarm(s)
While performing a Delete operation or Updating the status (Enable/Disable) of an alarm, the user can (optionally) provide the reason why the action is performed in a confirmation box. The same details will be logged in the Audit section.
Super Users and Normal Users, who have access to the Governance & Audit and Manage Alarm section can view the Alarm activity details under Environment Settings ->Governance Audit -> BizTalk360 Activities -> Alarm.
Note: Alarm Update Audit details contain the summary of updated values which include the previous value and the currently updated value.
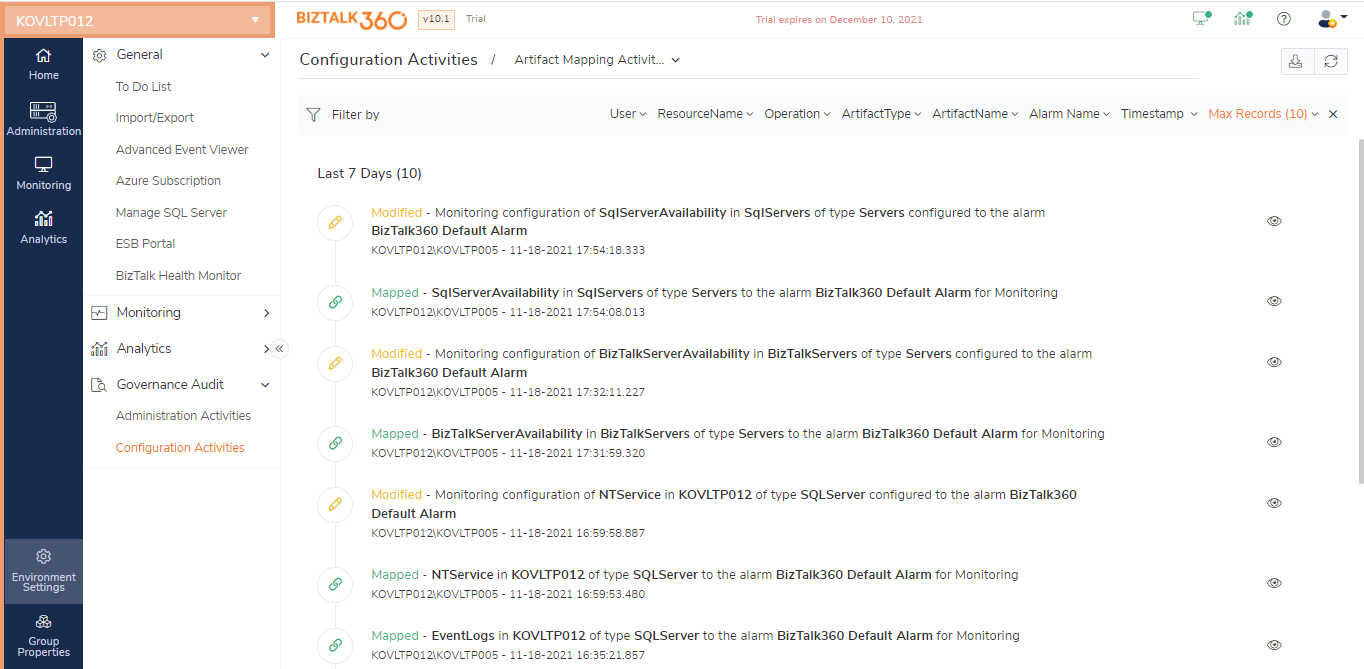
Manage Mapping audit
BizTalk360 has the capability to monitor artifacts such as BizTalk Application artifacts, BizTalk platform components, BizTalk Servers, Azure services, File Location, Queues, SQL server instances, and SQL servers.
Users can map the artifacts for monitoring to an alarm in the Manage Mapping section. The alarm will check for the current state of the mapped artifacts, and when a threshold condition gets violated, the alarm will send an alert.
The following operation activities, which can be performed from the Manage Mapping section, will be audited:
Map - When an artifact is mapped to an alarm and configured with threshold condition for monitoring
Modified - When threshold configuration of already mapped artifacts gets modified
Scenario 1 - Multiple Send Ports under one Application
When SendPort1 is mapped for monitoring, it will be audited as Mapping. When SendPort2, in the same application, is mapped for monitoring it will be audited as Modified.
Unmap- The artifacts which are mapped for monitoring can be unmapped from 2 sections:
From the Alarm mapping section (Monitoring -> Home -> Alarm Mapping)
From the Manage mapping section (Monitoring -> Manage Mapping)
When a user removes artifacts from being monitored, this will be audited as an UnMapped operation. Upon unmapping, a Confirmation pop-up will show up, in which the user can provide the reason for removing the mapping. The same details will be logged for auditing.
Scenario 2 - Multiple Artifacts under the same monitor type which are mapped for monitoring
Say multiple Send Ports under same the application are mapped for monitoring. When sendport1 is removed for monitoring, it will be audited as modified. When all the Send Ports are removed for monitoring it will be audited as UnMapped.
The above-mentioned scenarios are applicable for all the artifacts and monitor types.
On importing an alarm, the alarm will be audited under the Alarm Audit, and the mappings of the imported alarm will get audited under the Artifacts Mapping Audit section.
Secure SQL Query audit
Secure SQL Query functionality in BizTalk360 acts as a query repository in which SQL queries can be stored and executed. The queries can be accessed by BizTalk360 users without the need to access SQL Server Management Studio.
Since the queries are getting executed against SQL instances and databases, it is important to audit the Query operations.
Secure SQL Query auditing will log the below operations done at the Secure SQL Query section:
Create - The Create operation includes creating a new secure SQL query. Only users who have the SQL query permissions can create new secure SQL queries in BizTalk360
Delete - Only users who have the Delete Query permission can delete queries. Deleting the default (out-of-the-box) queries is not permitted in Secure SQL Query. When performing a Delete operation, a confirmation box will pop up in which the user can (optionally) provide the details of why the action is performed
Edit - Only users who have Edit Query permissions can edit custom SQL queries. Users are not allowed to edit the default (out-of-the-box) Secure SQL Query
.gif)
The Secure SQL Query audit details contain a summary of the audit which will provide a detailed view of the previous value and current value.
Super Users and Normal Users, who have permission to access Governance & Audit, Secure SQL Query section can view the Secure SQL Query operation activity details under Environment Settings -> Governance Audit -> BizTalk360 Activities -> Secure SQL Query.
BizTalk360 License Auditing
In BizTalk360, License activation and deactivation is the first major step involved before performing any other operation. Since we understand the importance of Licensing, it is important to give clarity to the customer, which user has activated or deactivated the license. Only superuser can view the licensed activity auditing details under Governance Audit -> BizTalk360 Activities -> License Audit.
License auditing will audit the below actions:
Activate - License Activation can be performed with an Internet connection and without an internet connection i.e. Activation/Manual Activation
Deactivate - License Deactivation can be performed with an Internet connection and without an internet connection i.e. Deactivation/Manual Deactivation
Remove – In case of new license update or change in license tier
For Normal user, they will not be able to view the License audit section, even if the governance audit permission is provided
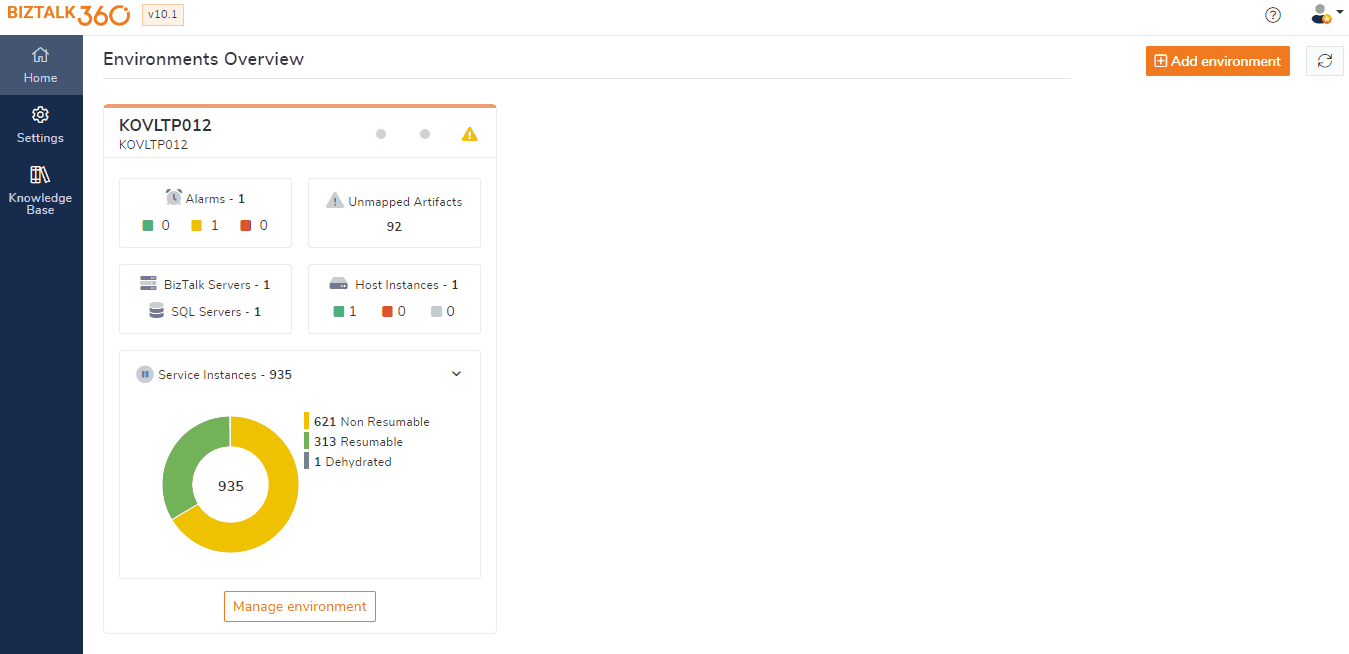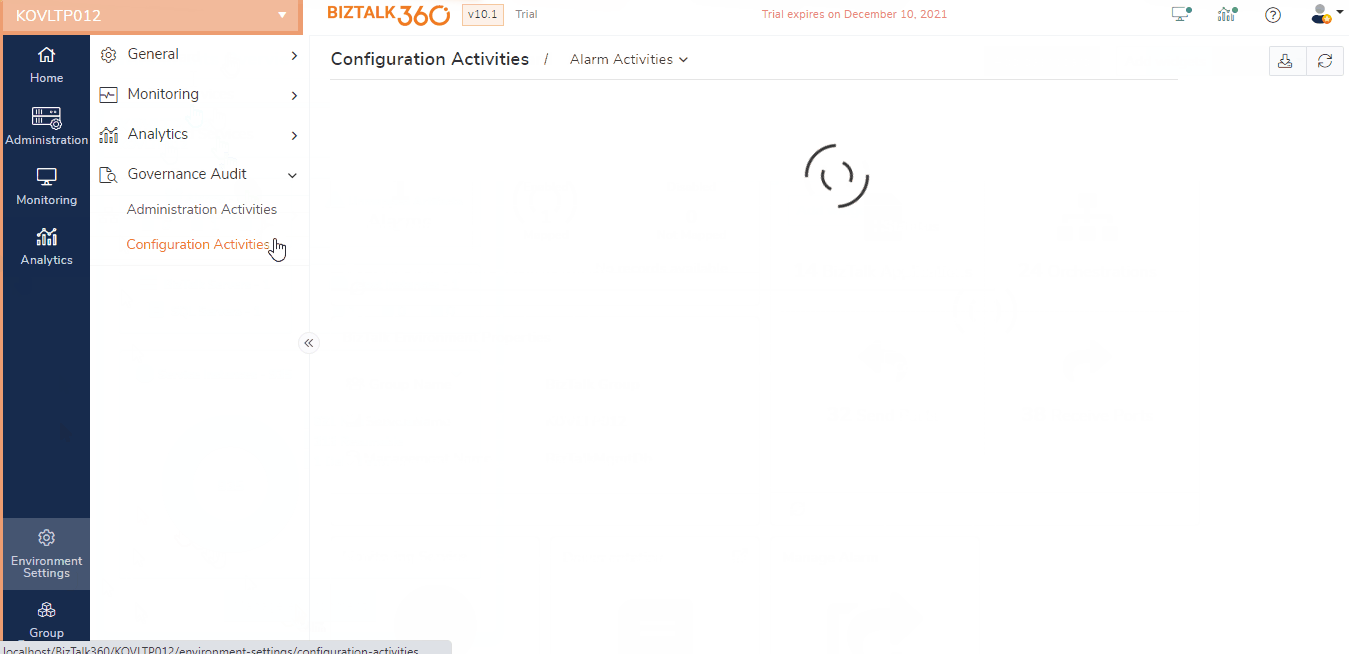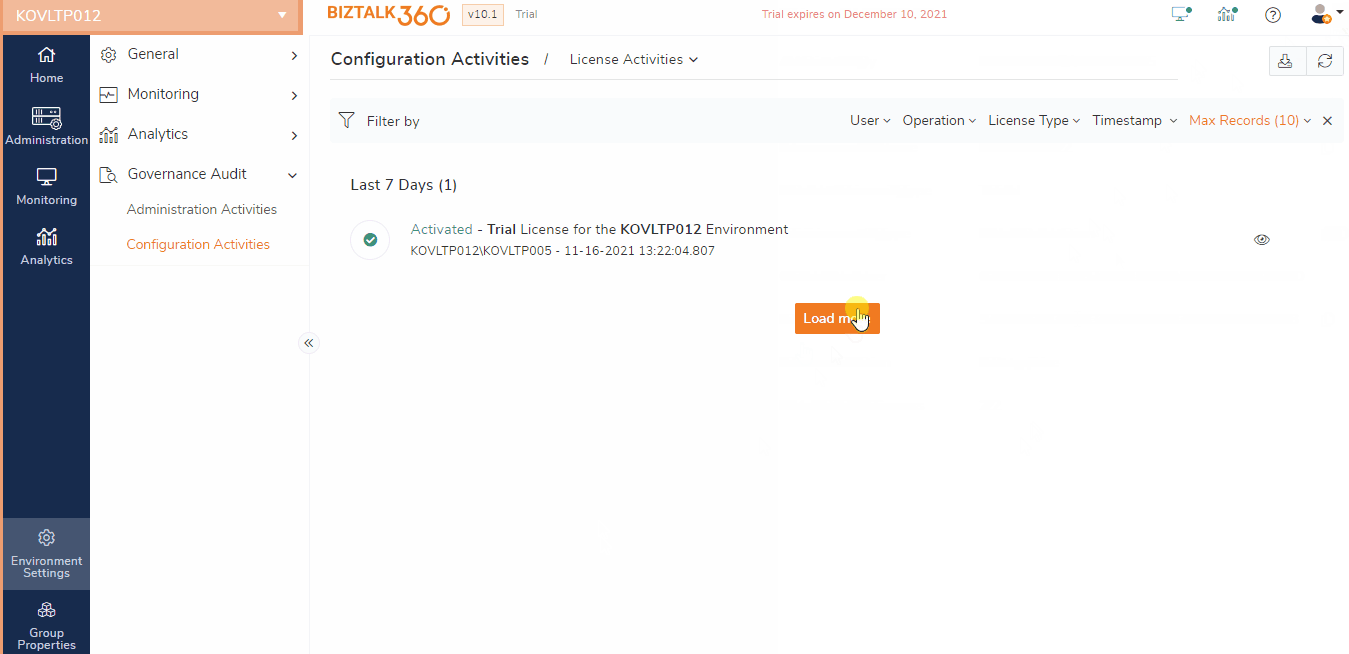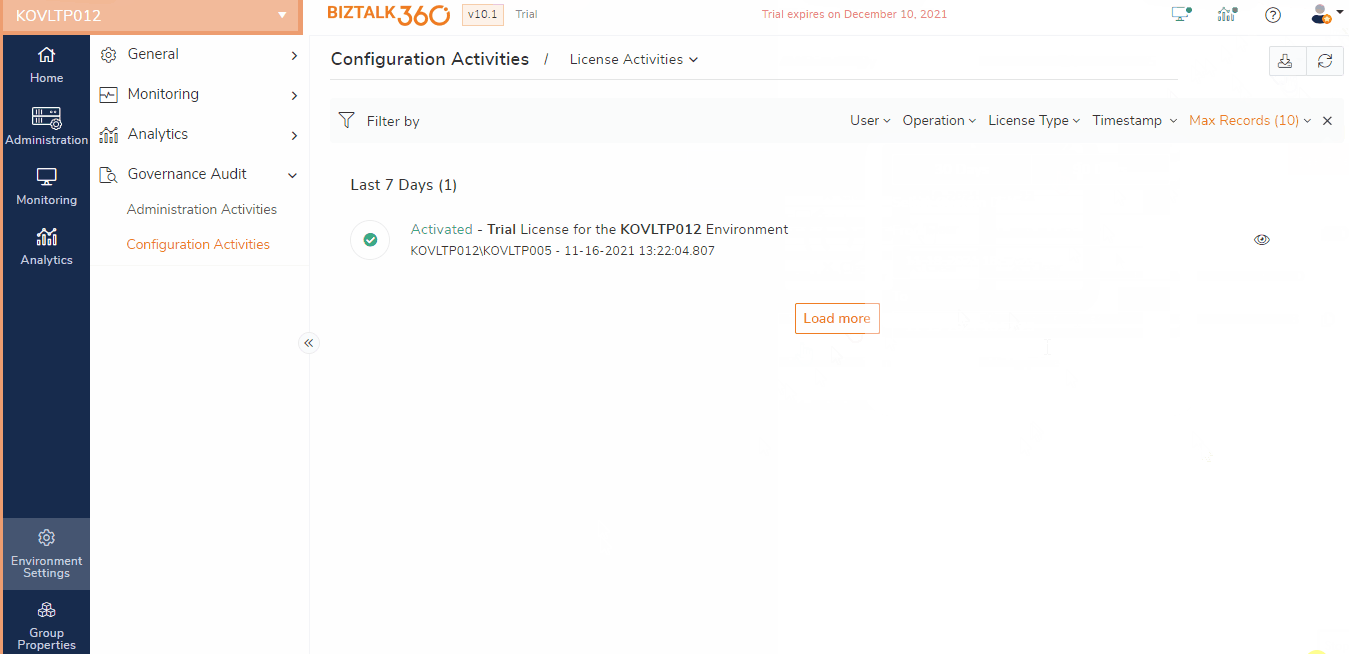
Scenario: Consider an environment has multiple user any user who has superuser permission can activate, deactivate or remove the license at any time. If one of the users deactivated the license in one environment and activated the same in another environment, then no other user under that environment can use the BizTalk360 application. Which may lead to lot many confusions. In such cases, the License auditing feature will be a helping hand to know what actually happened and which user has done the changes.
User Access Policy auditing
In BizTalk360, one of the important features is User Access Policies. These user policies allow to create sets of user profiles to decide which user has what permission in BizTalk360.
Manage user - Manage user feature allows the creation of Superuser, Normal user, and NT user, through which the user can set up access rights for users to different sections depending on the user requirements
Custom user profile - In this section, users can provide access to similar features to multiple users, by creating custom profile templates
Application groups - This allows you to create a group of the application as a predefined template and can use for different users as per their business needs
Manage Users
Manage Users in the User Access policy is the most sensitive section where any change in the user policies may lead to a major impact while accessing BizTalk360. The user may tend to change the permission based on the requirement, in which manual errors like selecting the additional feature or deselecting the required feature may lead to confusion and even has chances of deleting the user. This can be handled with the User access policy auditing feature.
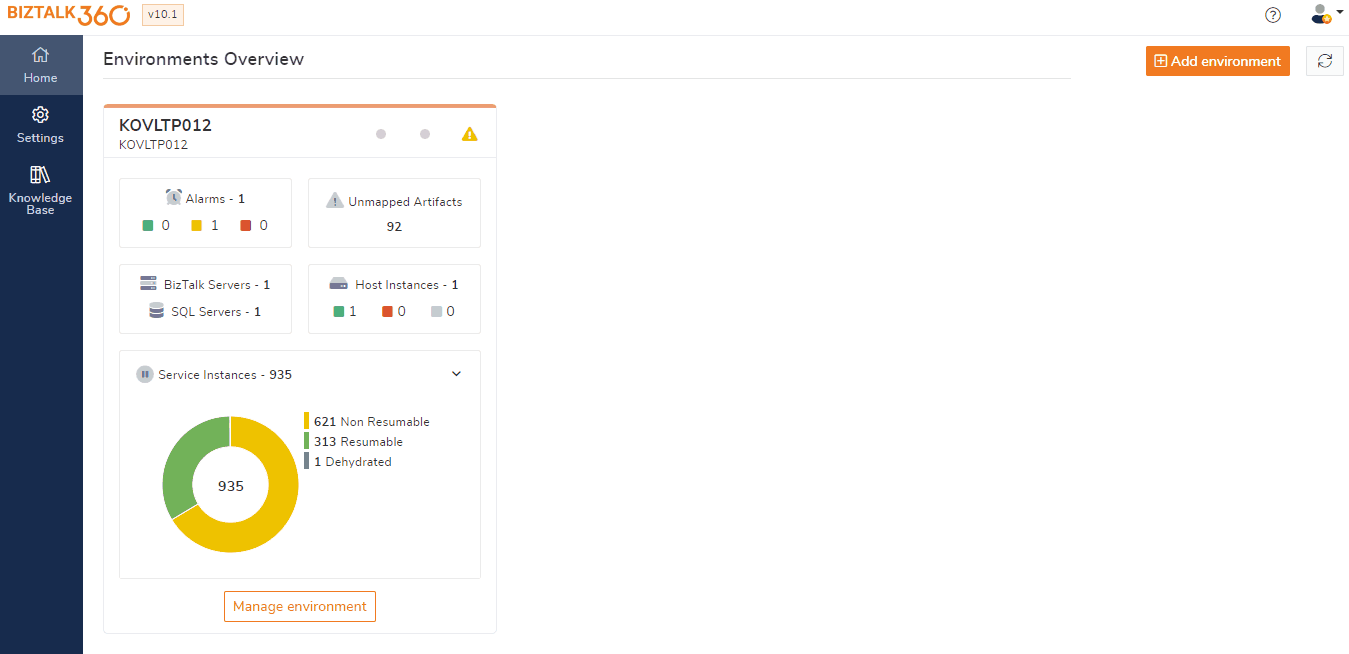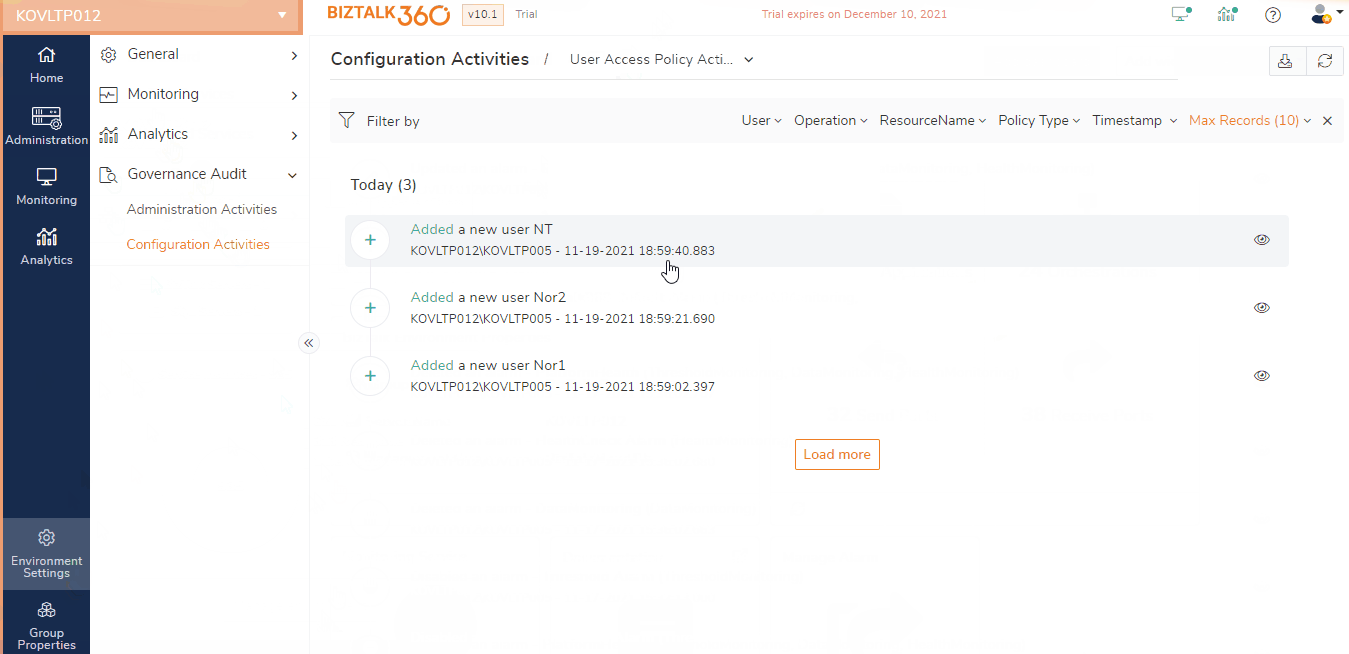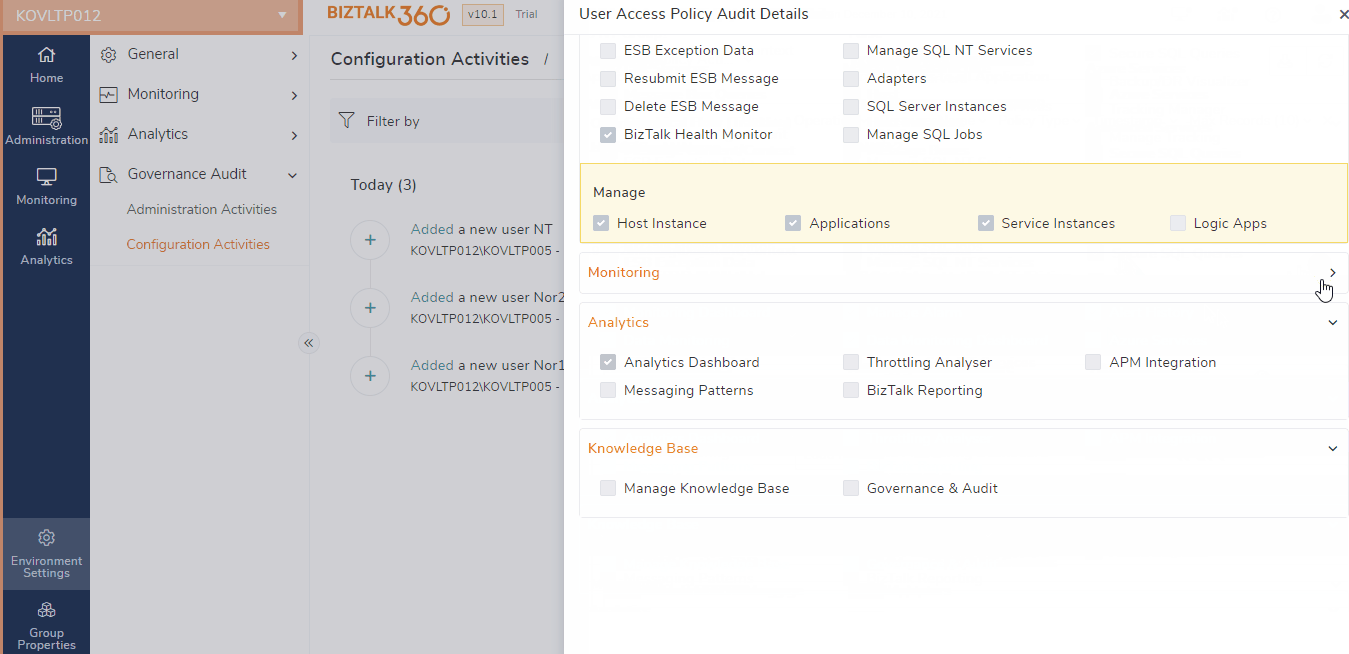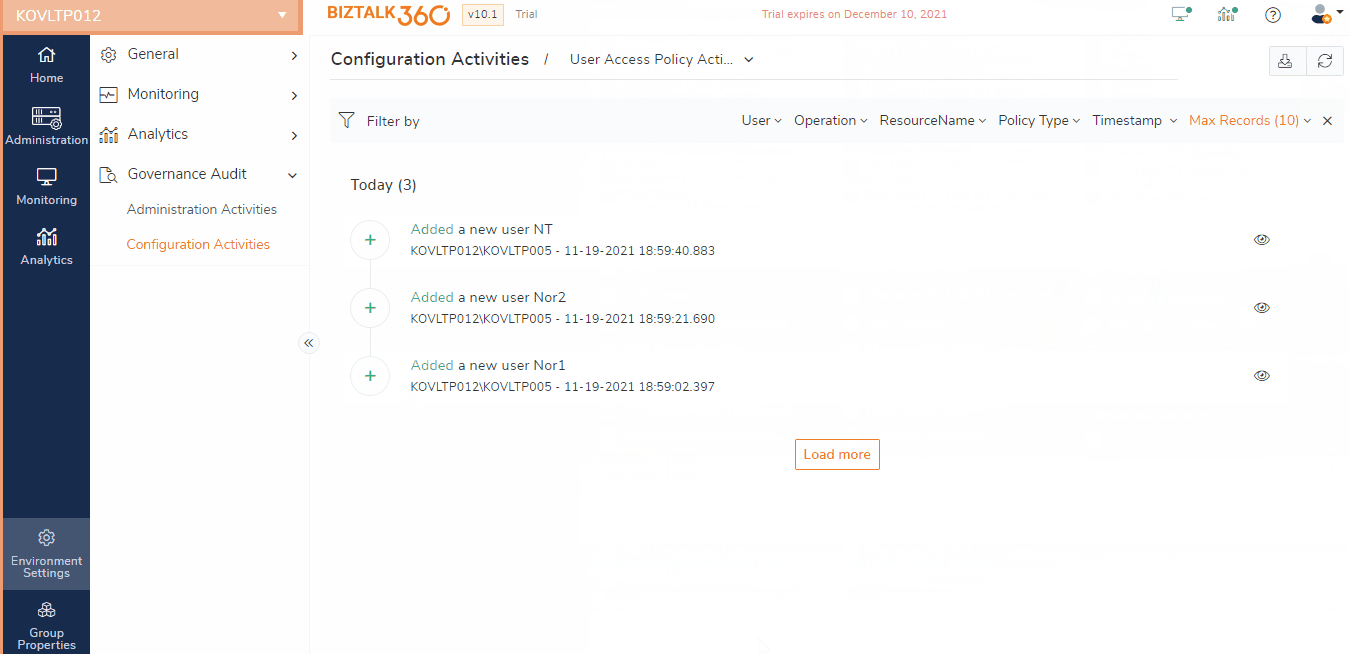
Super Users and Normal Users, who have access to the Governance & Audit can view the User Access Policy activity details under Environment Settings -> Governance Audit -> BizTalk360 Activities -> User Access Policy Audit.
Users access policy Activities will log the below operations done in the Manage users’ section:
Add - On adding a new user the operation will be logged in the auditing section. The user who has super user permission are allowed to create users
Update - A super user is allowed to edit the user by adding or removing the permission for accessing the BizTalk360 features and can also edit the access on application
Remove - A super user is allowed to remove the user by clicking on the delete button
Switch user - A super user can change the role between the users, you can either switch the role from Normal user to Superuser or from Superuser to Normal user
Manage Custom User Profiles:
Custom User Profile provides you to access similar features to multiple users by creating custom profile templates. The users may belong to different groups yet require similar permissions to access BizTalk360.
Users access policy Activities auditing will log the below operations done in the Manage Custom User Profiles section:
Create - Create operation will audit custom user profile creation
Update - Update operation includes changing the description and on add or remove profile permission will be audited
Delete - Delete operation will audit when deleting the custom profile
The user who as supper user permission are only allowed to create the Custom profile.
Application Groups:
Application Groups allows for the creation of groups and map the related applications to these groups. Say, for instance, all applications related to banking can be grouped under an application group name and can map the same to the appropriate users to access this Application Group.
Users access policy Activities auditing will log the below operations done in the Manage Application groups section:
Create: Create operation will audit application group creation.
Update: Update operation audit on add or remove application permission.
Delete: Delete operation will audit when deleting the application groups.
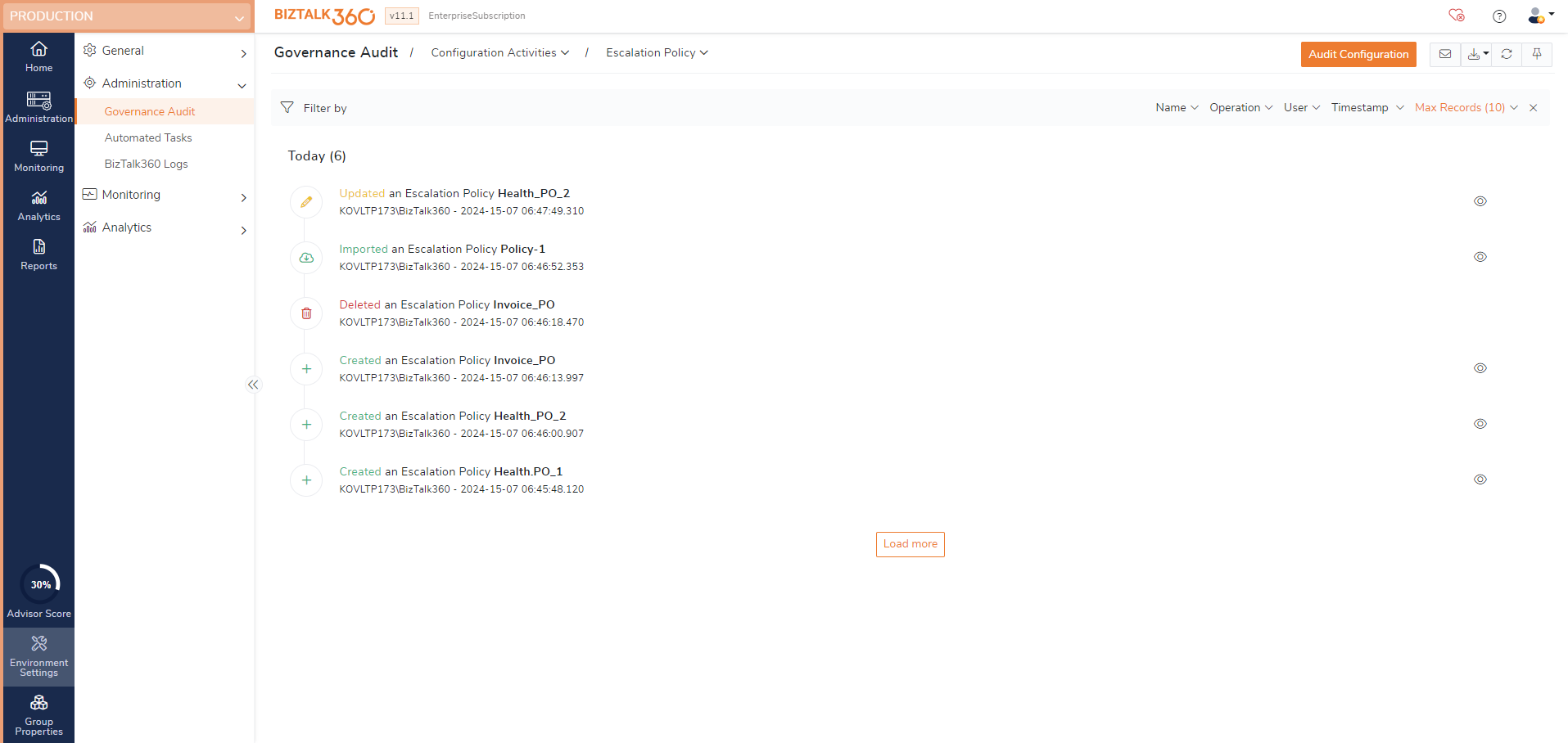
Escalation policy auditing
With the BizTalk360 escalation policy, an incident is generated for every violation, and it escalates if no action is taken within a specified timeframe. For instance, if a crucial receive or send port in your BizTalk Server environment fails, it can interrupt the flow of message transactions and halt business processes. In such situations, the escalation policy helps ensure smooth message transactions by promptly addressing the issue.
Escalation policy related activities are audited and will log the below operations done in the escalation policy section:
Create - Creating an escalation policy will be audited.
Update - Updating an escalation policy will be audited.
Delete - Deletion of an escalation policy will be audited.
Import - Importing an escalation policy will be audited.
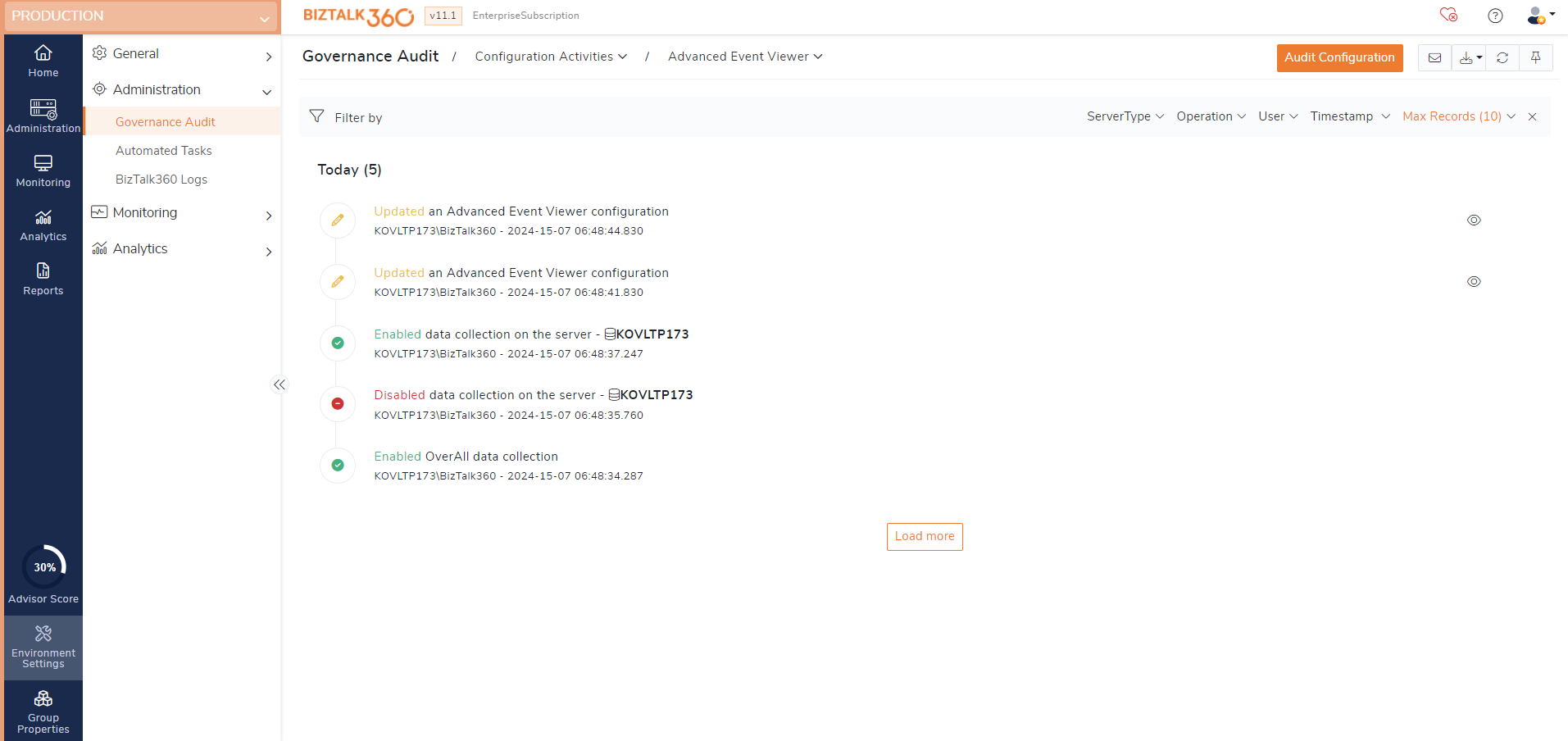
Advanced Event Viewer auditing
Enabling BizTalk360's built-in Advanced Event Viewer (AEV) allows you to gather event data from any server within your environment and display it on a single screen, where you can use the rich query capabilities to search and analyze the data.
Activities related to advanced event viewer are audited and will be log the below operations in governance and audit section. This helps business users to track activities happened with respect to their SQL servers in their business environment.
Enable - Enabling advanced event viewer will get audited.
Disable - Disabling advanced event viewer will get audited.
Update - Updating the event sources in advanced event viewer will get audited.
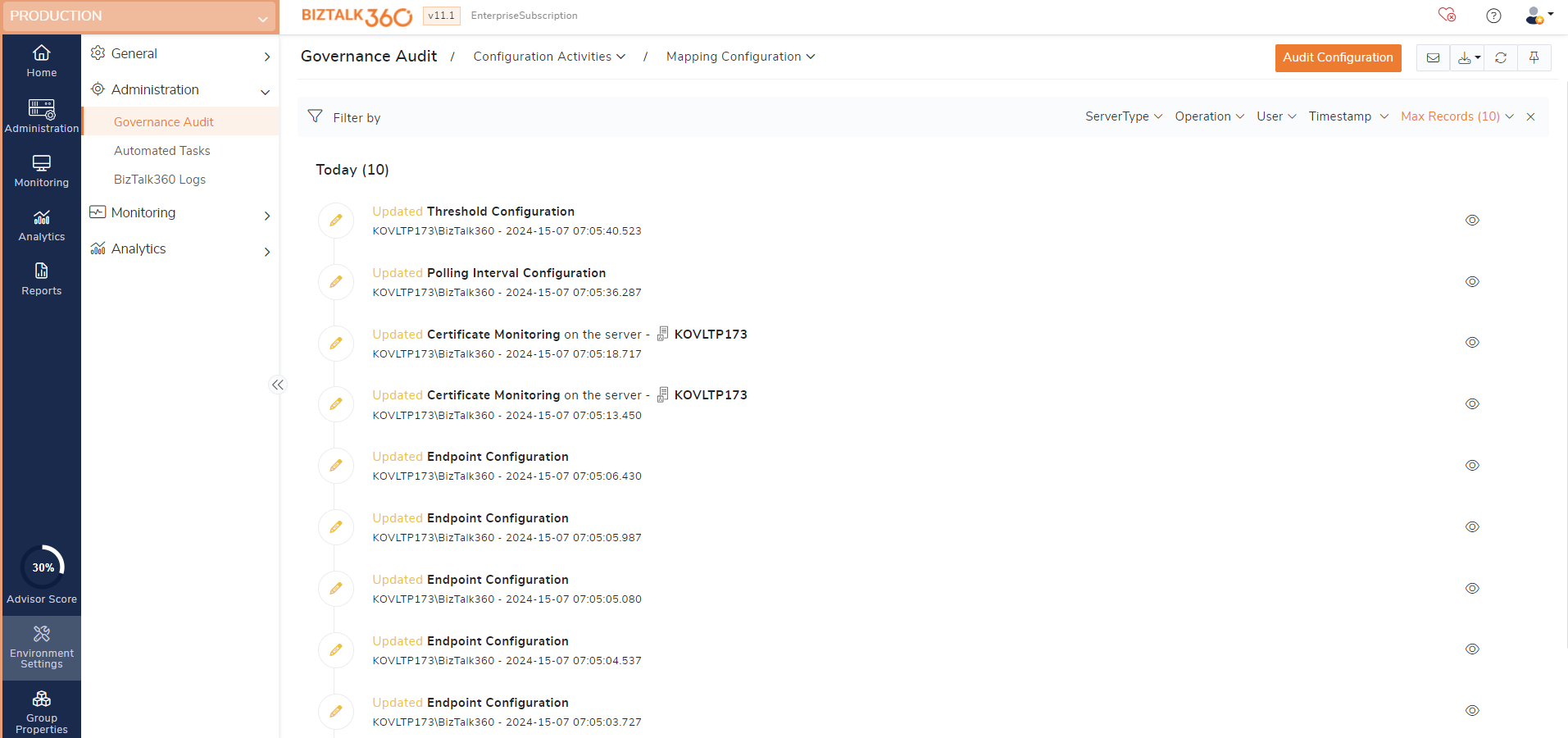
Mapping configuration auditing
In Mapping configurations page, users can provide default values for polling intervals, threshold, endpoints and certificate monitoring. Updating values of the below configurations are audited to keep track of the changes made in the below areas.
Polling interval - Updating the values of polling intervals will get audited.
Threshold Configuration - Updating the values of threshold monitoring for disks, system resources, BHM and service instances will get audited.
Endpoint configuration - Enabling or disabling the endpoint configurations for file, FTP, SFTP and IBMMQ will get audited.
Certificate monitoring - Enabling, disabling of certificate monitoring and updating the certificate stores will get audited.
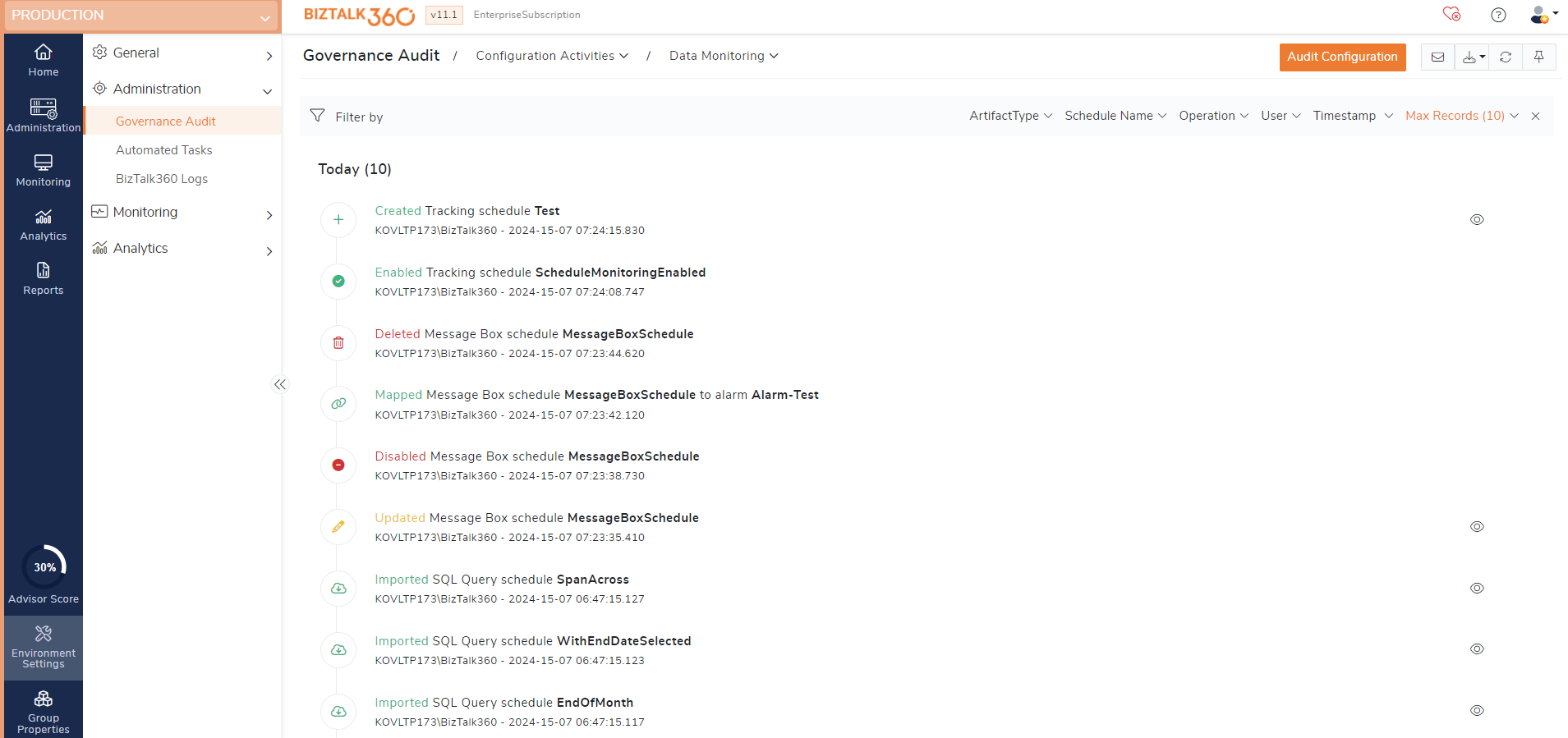
Data Monitoring auditing
Monitoring the health of an integration platform or BizTalk environment is essential for smooth business operations. If any artifact encounters an issue, it can disrupt the entire business process. Both the system artifacts and the transmitted data are crucial for maintaining a healthy environment.
It's important to ensure that data flows correctly, verify successful transmissions, and check if the expected number of files are processed within a certain timeframe. This is where BizTalk360's data monitoring feature helps. Users can set error and warning thresholds to monitor data points and receive notifications if these thresholds are exceeded. Hence, monitoring or keeping track of the activities performed related to data monitoring is also important.
The below activities that happened with respect to data monitoring are audited and will be logged for any references.
Create - Creating a data monitoring schedule will be audited.
Update - Updating the alarm name, schedule name, query type, filters, threshold conditions and monitoring schedule of a data monitoring schedule will be audited.
Delete - Deleting a data monitoring schedule will be audited.
Enable - Enabling a data monitoring schedule will be audited.
Disable - Disabling a data monitoring schedule will be audited.
Reset Next run - Resetting the next run of a data monitoring schedule will be audited.
Map to other alarm - Mapping data monitoring schedules to another alarm will get audited.
Import - Importing a data monitoring schedule will be audited.
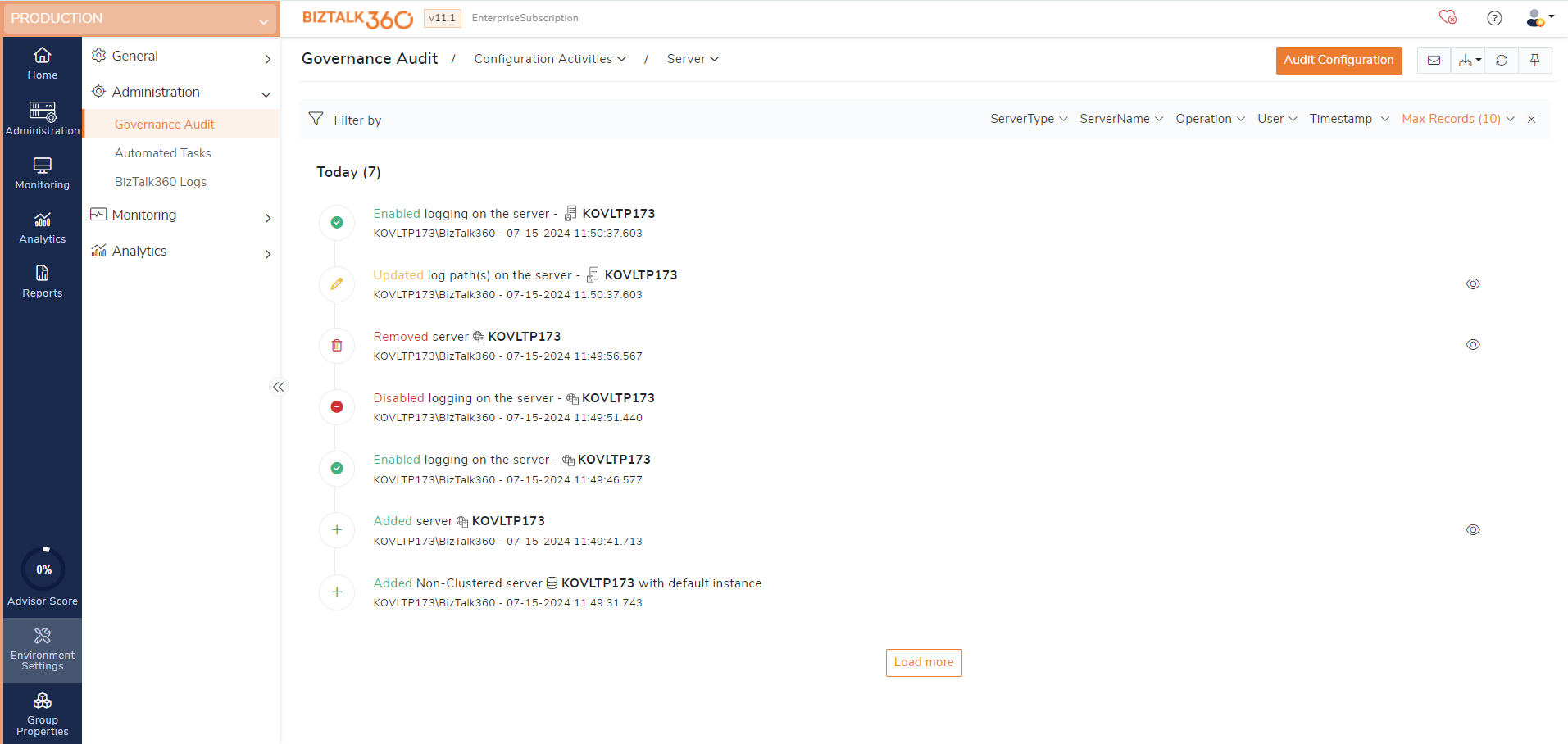
Server operations auditing
Regular server-related activities, such as monitoring and maintenance ensure optimal performance and prevent downtime. Auditing provides a record of all actions performed on the server, ensuring the security of the business environments. The below activities performed in the BizTalk server, SQL server and IIS servers are logged under server.
BizTalk server - Updating the BizTalk server logs will be audited.
IIS server - Adding, updating and deleting IIS servers will get audited. And enabling / disabling the IIS logs configuration will also get audited.
SQL server - Adding, updating and deleting SQL server and instances will be audited.
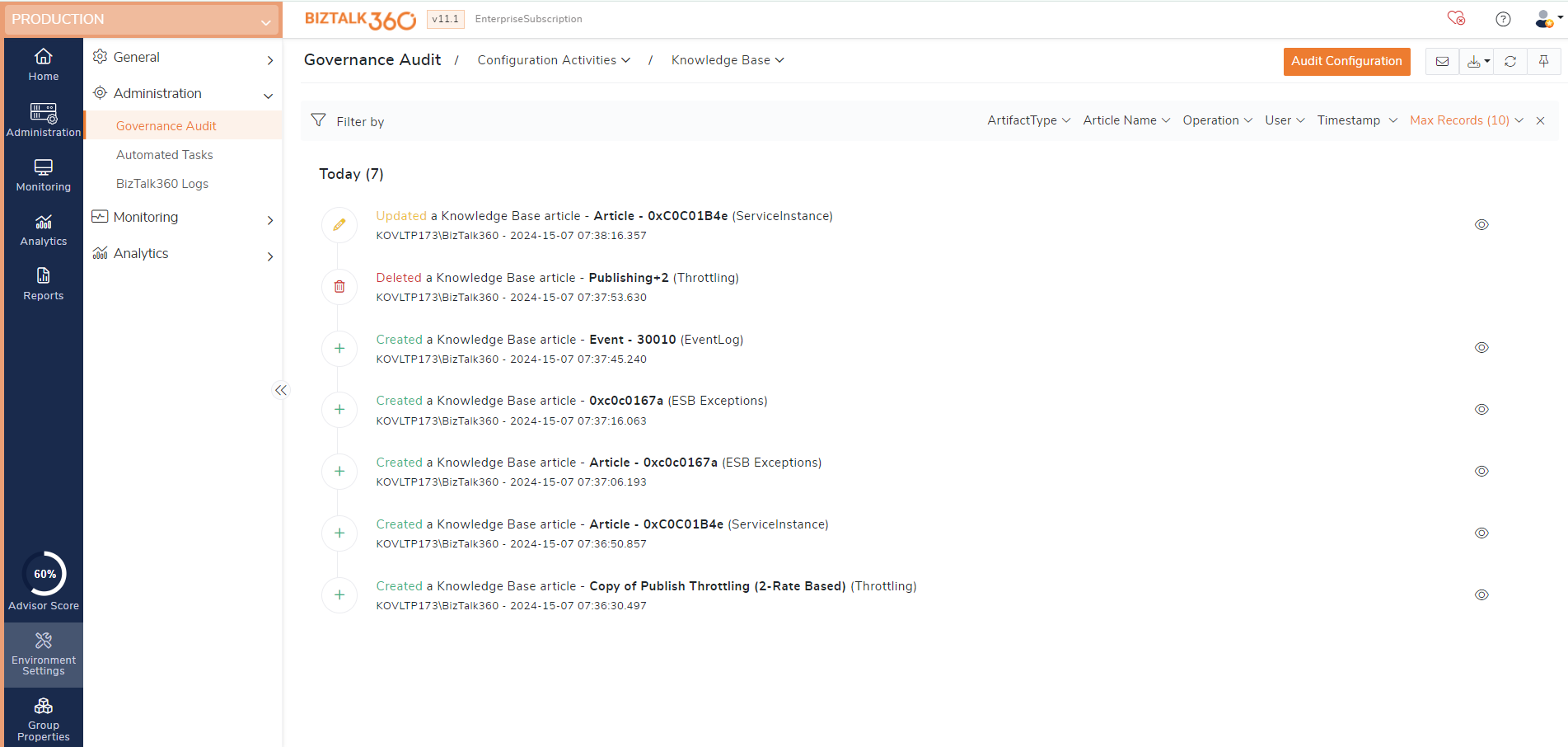
Knowledgebase operations auditing
When an issue occurs in BizTalk resulting in a Suspended instance, it will have an associated error code. Using this error code, you can document the solution for each issue. Additionally, you can use criteria such as the BizTalk application, Service name, and parts of the Error Description to link an article to a specific issue. Similarly, BizTalk360 allows you to document issues related to Event Log entries, Throttling data, and ESB exceptions.
Keeping eye on changes made in the existing articles and addition of new articles are crucial. The below activities with respect to knowledgebase performed will be logged for future references.
Create - Creating a knowledge base article for service instancess, ESB, Event log and throttling are audited.
Update - Updating the name, error code, template, environment name, host name, exception details of a knowledge base articles for service instances, ESB, Event log and throttling are audited.
Delete - Deleting the knowledge base articles of service instances, ESB, Event log and throttling are audited.
Import - Importing the knowledge base articles of service instances, ESB, Event log and throttling are audited.
Clone - Cloning the knowledge base articles of service instances, ESB, Event log and throttling are audited.
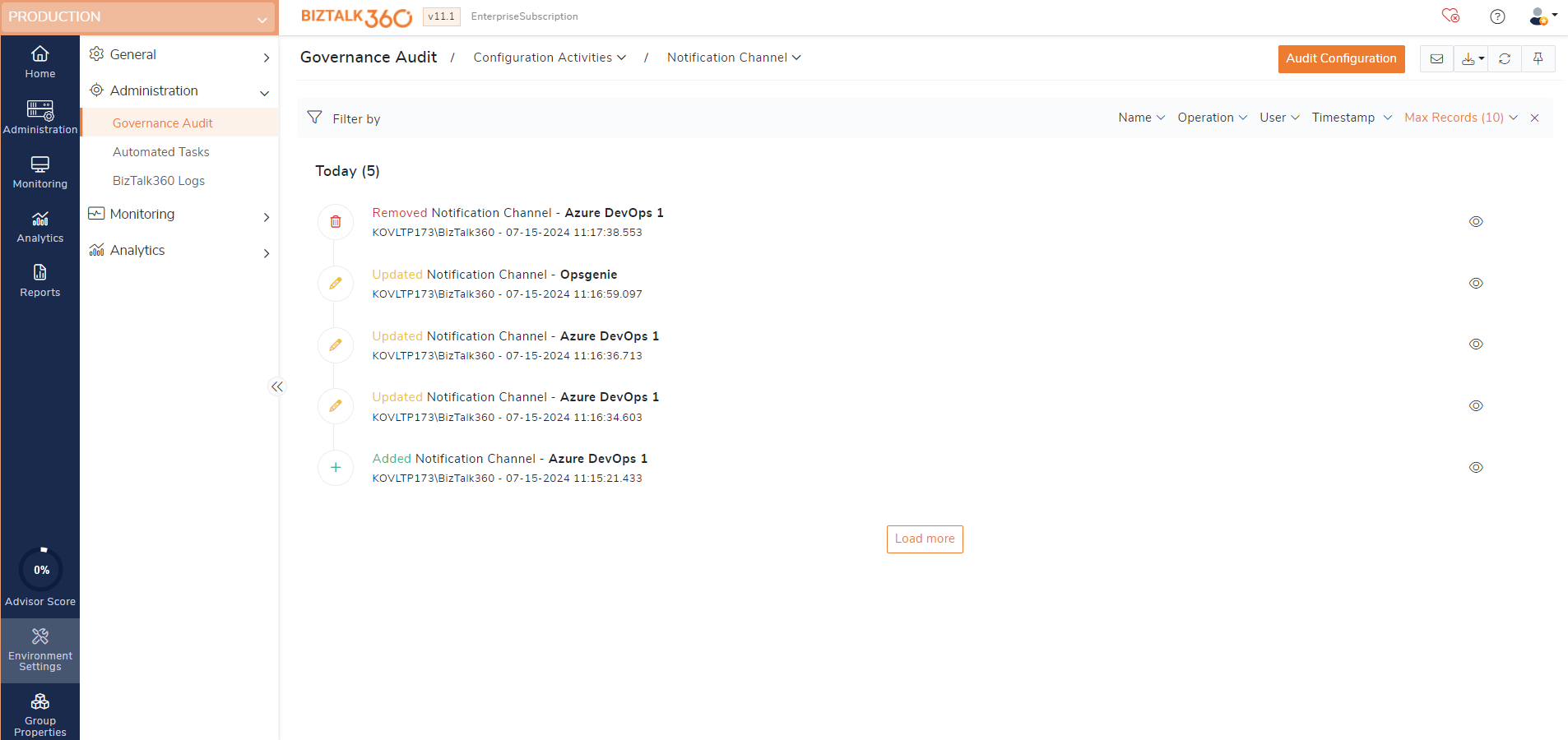
Notification channels auditing
Notification channels ensure that critical alerts and updates are delivered promptly to the business users allowing them to take necessary actions against the issues. Auditing the activities of notification channels can help detect unauthorized access or suspicious activities, enhancing the overall security of the application.
Notification channels audit involves auditing the below activities.
Create - Creating new notification channels will get audited.
Update - Updating the name, DLLs, and credentials of the configured notification channels will get audited.
Delete - Deleting a notification channel will get audited.
Enable - Enabling a notification channel will get audited.
Disable - Disabling a notification channel will get audited.
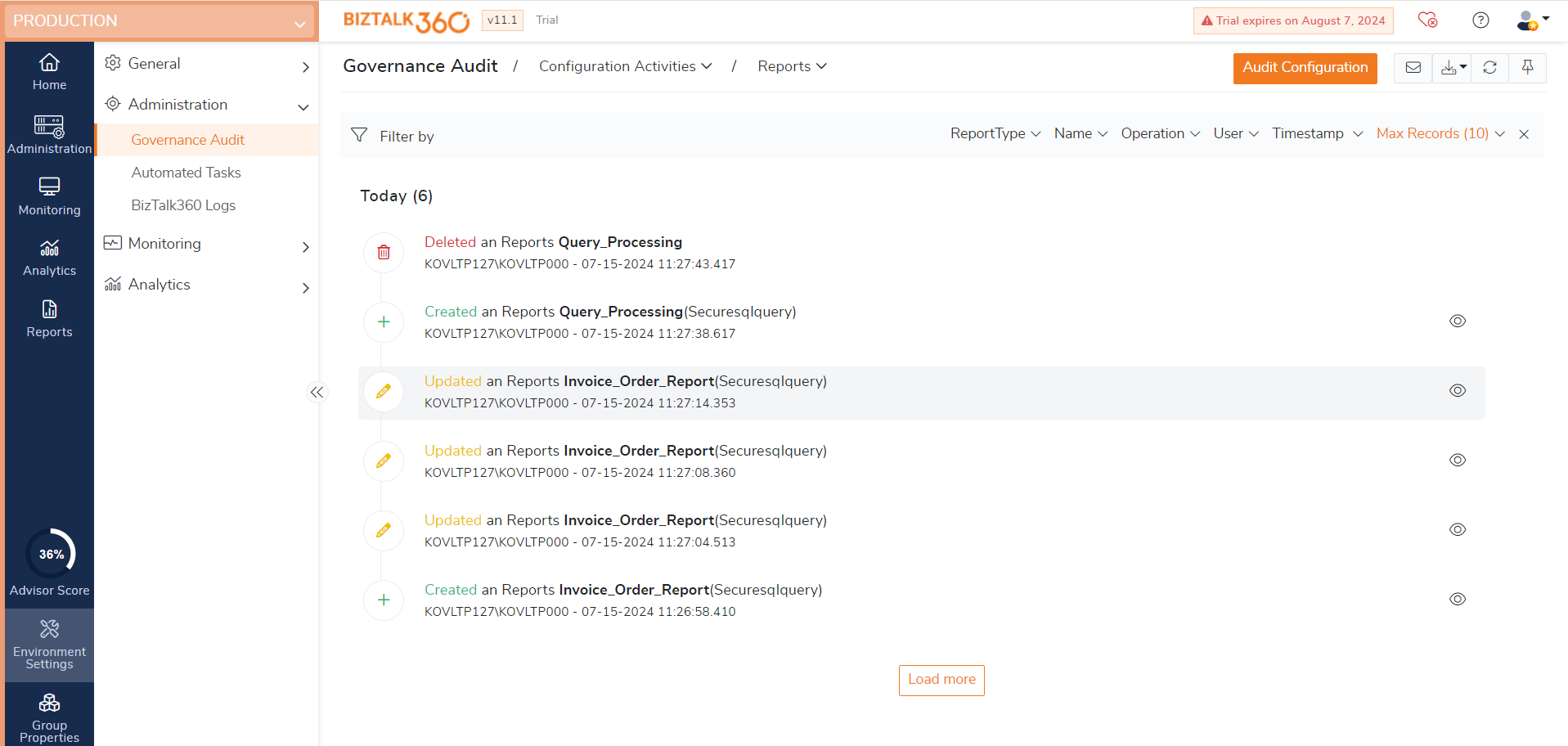
Reports Auditing
Reporting enables users to receive configured dashboards or Secure SQL query results as PDF documents on a regular basis, according to the scheduled configuration. Auditing reports is essential to maintain the security of data.
Create - Creating reports will be audited.
Update - Updating the name, type of dashboard / SQL query, report schedule and notification settings will get audited.
Delete - Deleting a report will get audited.
Enable - Enabling a report will get audited.
Disable - Disabling a report will get audited.
Import - Importing a report will get audited.
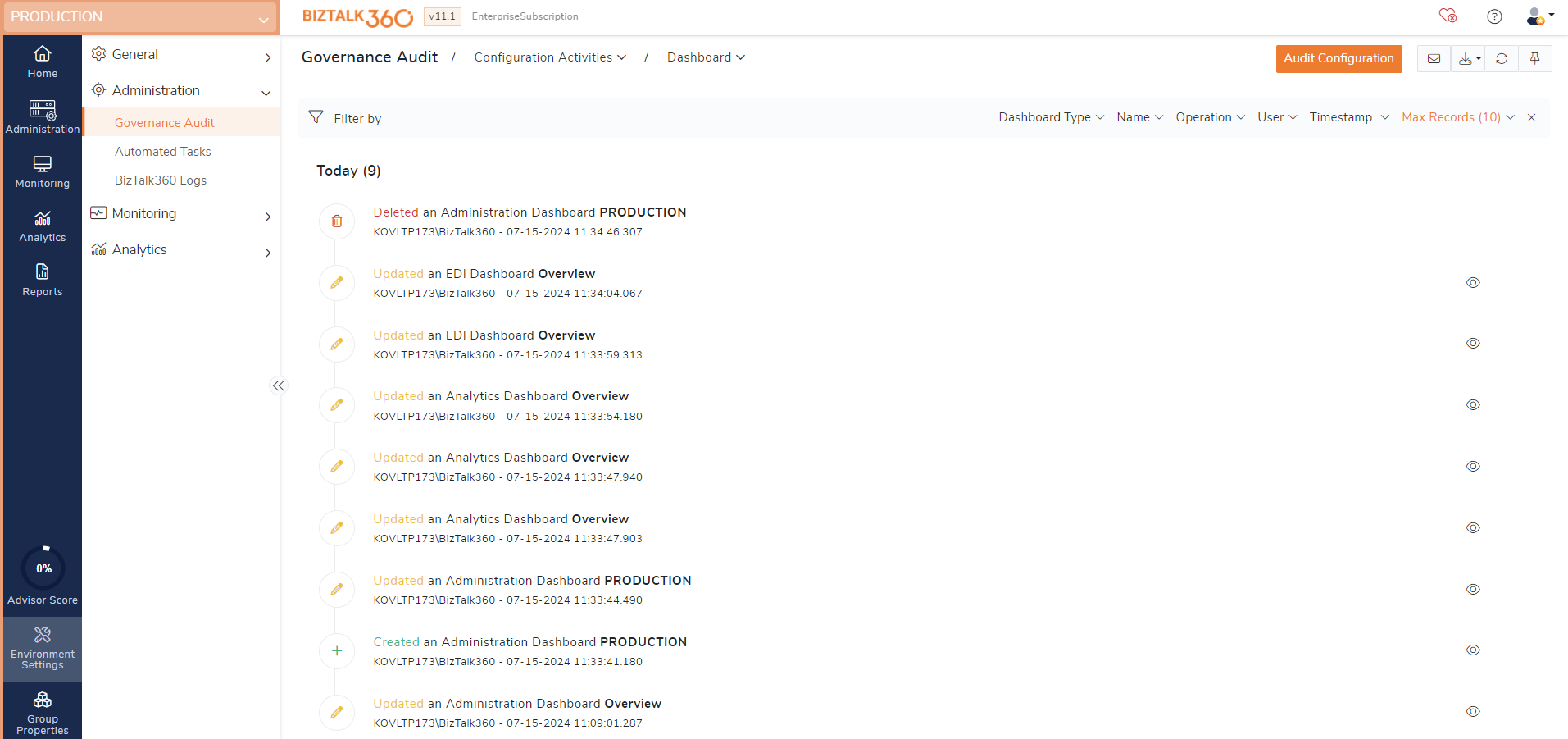
Dashboard operations auditing
Any configuration level activities done in administration, EDI, ESB and analytics dashboard will be audited. This helps users to track the configuration level changes made by several users in their business environment in a single place.
Create - Creating dashboards in the administration, EDI, ESB and analytics sections will get audited.
Update - Updating the name, setting it global, adding widgets, editing widgets and customizing administration, EDI, ESB and analytics sections will get audited.
Delete - Deleting dashboards in the administration, EDI, ESB and analytics sections will get audited.