PowerShell scripts can be used to automate many of BizTalk Server administrator tasks and also the scripts are used to manage the BizTalk Environment for various reasons.
Let us consider a scenario where the BizTalk server solution is deployed to a different environment and for some reason, you can't use CI/CD . Then the PowerShell script can be used to change the URI of all the ports from the binding files and also with the script you can update the authentication credentials of each port. This execution can be scheduled by using BizTalk360 PowerShell Automated Task.
Any PowerShell script created in the local or remote server can be mapped for execution. BizTalk360 PowerShell Task will validate and execute the mapped script during the scheduled time.
PowerShell task Configuration
To configure PowerShell Tasks, navigate to Environment Settings->Automated Tasks ->New Task Configuration->Select PowerShell Script, which will open the task configuration blade
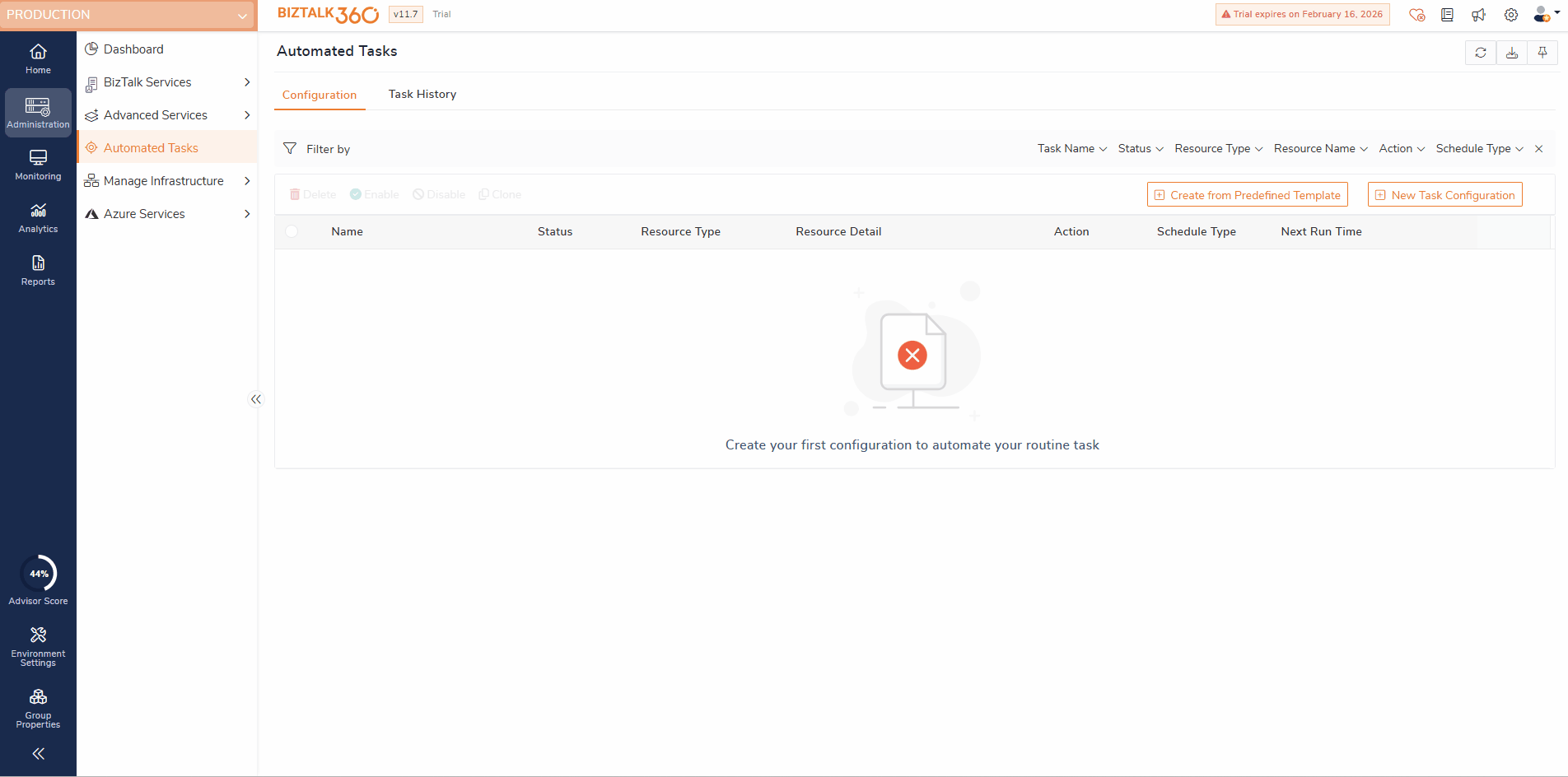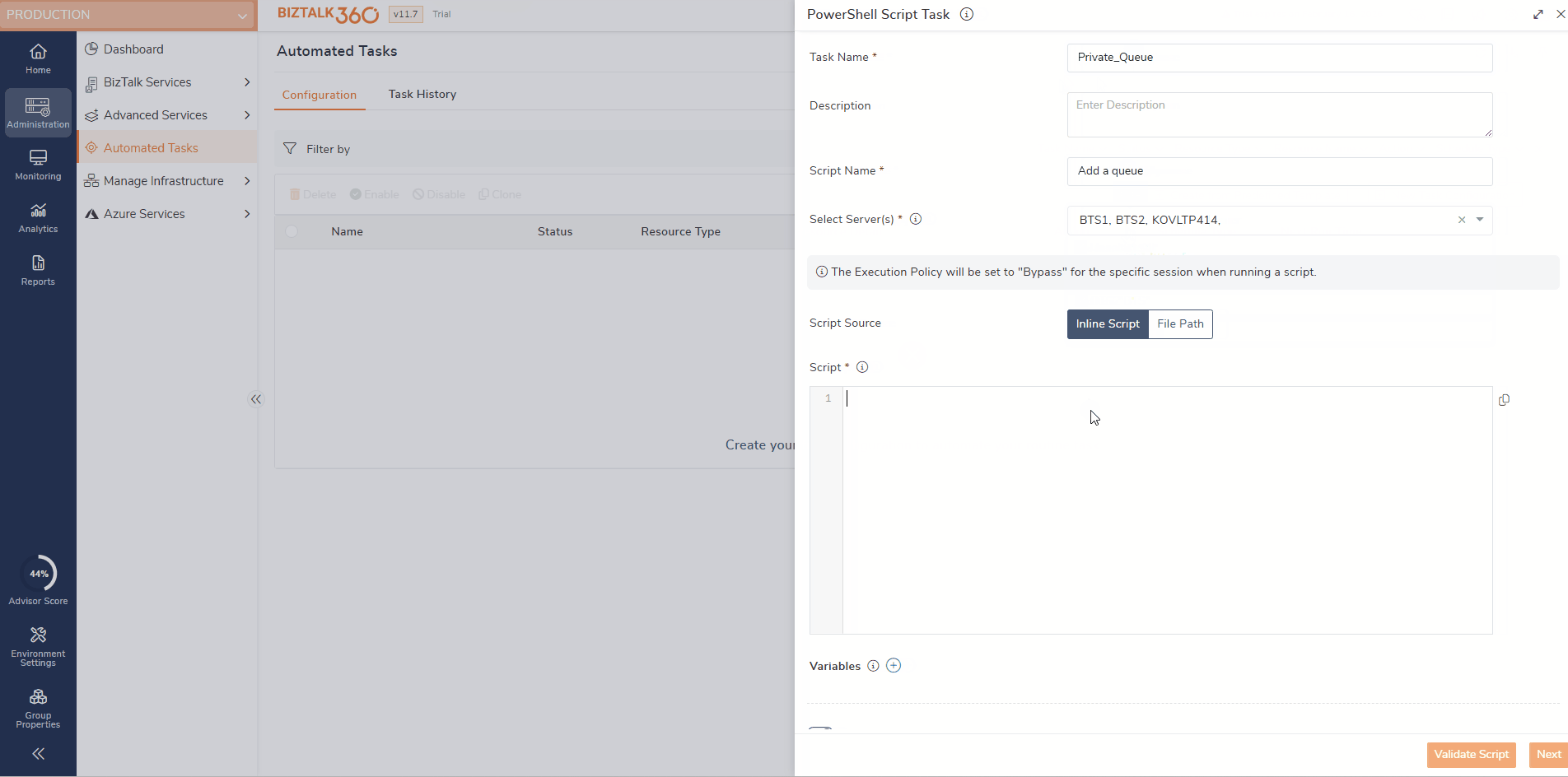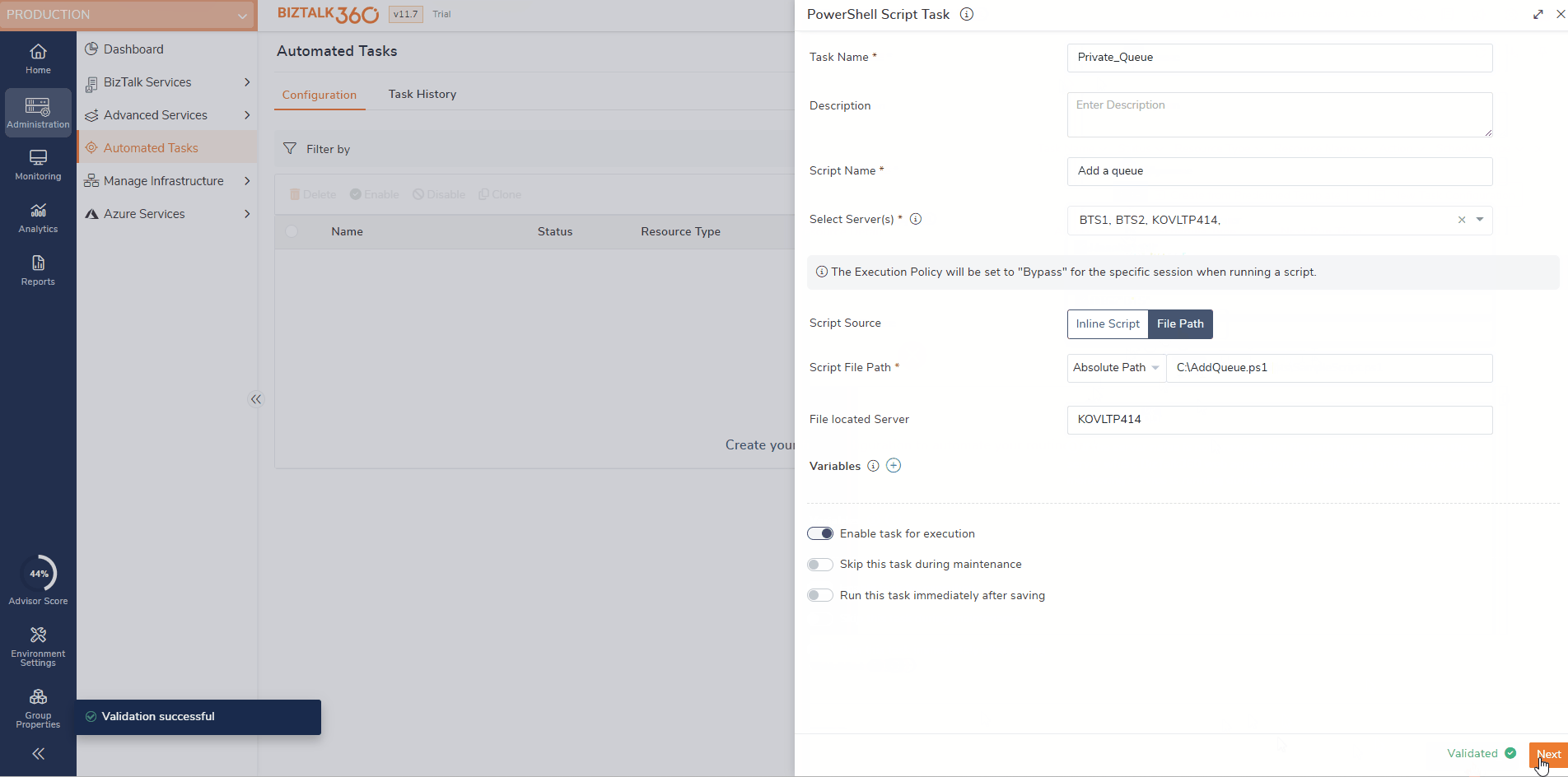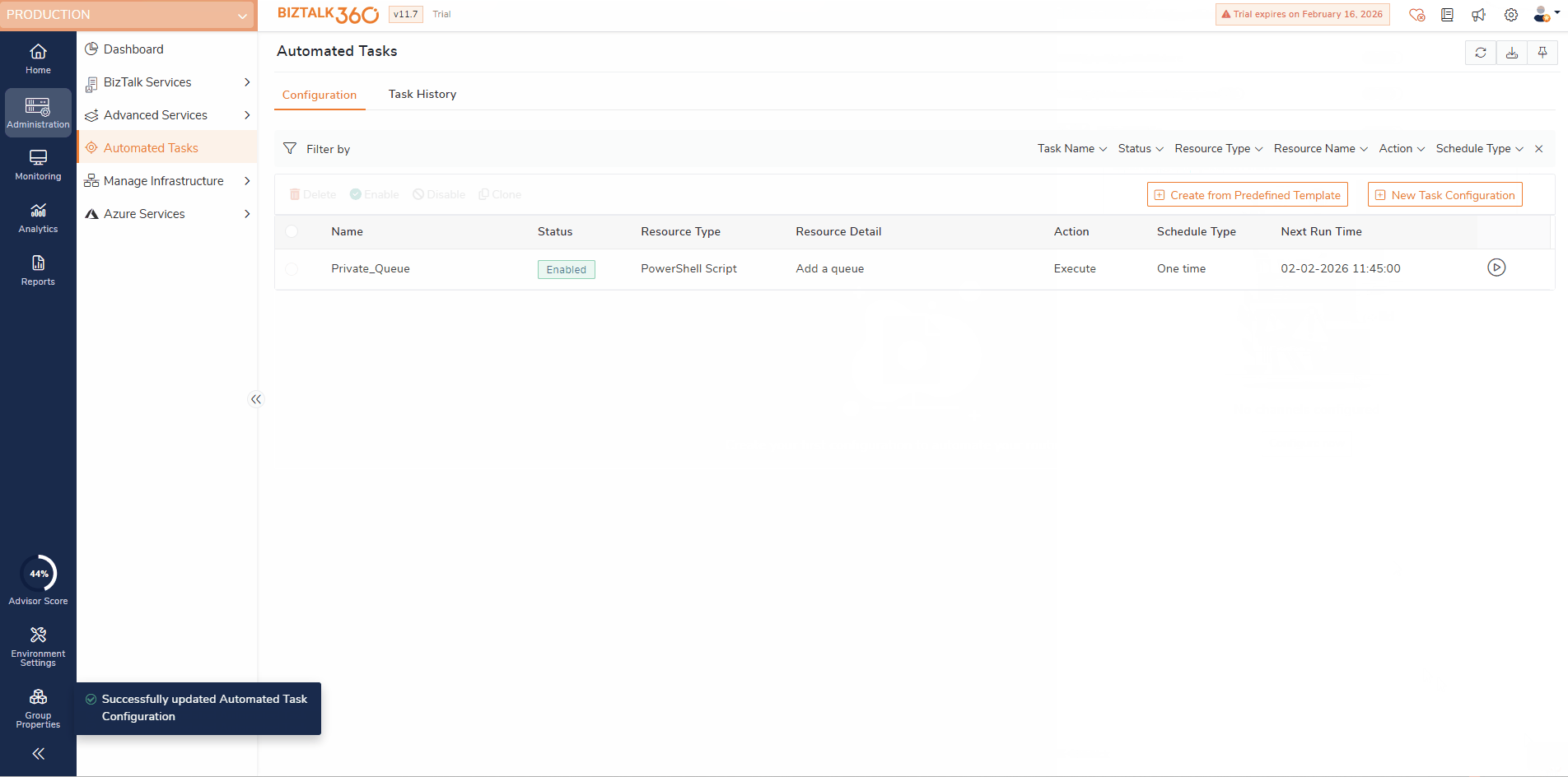
Add the Task Name and Description
What happens if the server is not reachable?
The task can be still saved even when the server is not reachable, but the script execution will get failed.
Script Name-Provide a friendly name for your identification
Server - Enter the server names (Local/Remote) where the PowerShell Script needs to be executed, maximum of 5 server can be added. The user must have access to the server for script execution.
Script Source- Update the script source Inline Script / File Path.
Inline Script - if inline script is selected, provide the script that need to be executed.
File Path - When File Path is selected, the PowerShell script is executed from an existing
.ps1file stored on a server.Path Type Selection
Absolute Path – Full path from the root directory
Relative Path – Path relative to a predefined working directory
Script File Path
Provide the full or relative path of the PowerShell script file (
.ps1).
Server Name
Specify the server where the script file is located.
The execution account must have read permissions on the script file.
View Script Result - Using the 'Write-Output' and 'Write-Error' commands allows you to view the script output in both Notification and Task execution history.
Example , Below is a sample script to view the file count. By adding 'Write-Output', the file count will be listed in the Automated Task notification.
# Define the folder path
$folderPath = "D:\BizTalkArtifacts\FileSP"
# Get all the files in the folder
$files = Get-ChildItem -Path $folderPath -File
# Count the number of files
$fileCount = $files.Count
# Output the results
Write-Output "There are $fileCount files in the folder $folderPath."
Variable - Add the values for the variable that is mentioned in the script. Add a variable in the same order as updated in the script. If a variable is dependent on another variable, make sure that is updated first
Validate Script this option helps to validate the script syntax and throws an error
Task Execution Setting
Enable/Disable Task: By default, the task execution will be enabled. You can disable it if needed which stop the execution.
Skip During Maintenance: Enable this option to prevent the task from executing during the maintenance period.
Run Immediately: Enable this option to run the task immediately after saving the configuration. However ,the task will also execute at the scheduled time.
Notification Configuration - Enable the channels in which you wish to get notified about the script execution
On successful task configuration, you can see the task in the configuration grid along with the task name, resource type, resource details, Action, Schedule type, and Next execution time.
Task History:
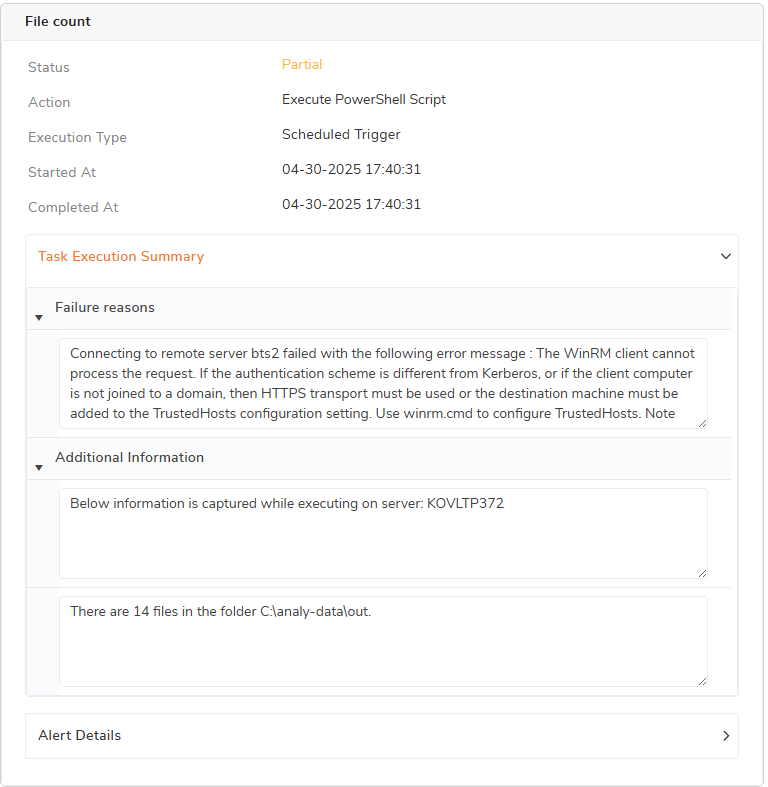
Once the task is configured, the given script will be executed in the specified servers at the scheduled time. During the execution in case if any of the specified server is not reachable or any permission issue detected, those will be captured and mentioned in the Task history. System sends alerts along with the successful execution of remaining servers.
The Task History will be shown as below, failed execution error details will be given in the Failure reason section, and the output of successful execution will be shown in the Additional information section. The same details will be shown in Alert as well.
Points to Remember:
Monitoring service should run under the administrator account
The user must have access to the server in which the PowerShell Script gets executed
The connection to the remote server is made via Telnet or Ping (ICMP). Make sure the BizTalk360 running servers should be enabled with the ports Telnet - TCP/23, Ping ICMP/Protocol-1 in the Windows Firewall to communicate with the other server.